
Fashion waste is an escalating environmental issue that poses a significant threat to our planet. The fashion industry is responsible for generating substantial waste annually, including discarded garments and leftover materials from production.
New solutions and eco-friendly practices are being implemented to address this problem. One example is the use of leftover fabric, also known as deadstock. This helps to reduce waste and promote sustainability in the fashion industry. By utilizing deadstock, companies can minimize their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Using deadstock fabric with apparel PLM software helps reduce fashion waste. This improves resource management and supply chain sustainability. It is a sustainable way to make a positive impact on the environment.
This article talks about using deadstock fabric and sustainable materials to reduce waste. It also explains how fashion PLM software can assist in improving these sustainability efforts.
Understanding Deadstock Fabric
Deadstock fabric refers to surplus or leftover fabric from manufacturers and designers that is no longer in active production. People often discard or leave unused these fabrics, contributing to the growing problem of textile waste. Deadstock fabric can originate from various sources, including overproduction, discontinued lines, cancelled orders, or remnants from the cutting process.
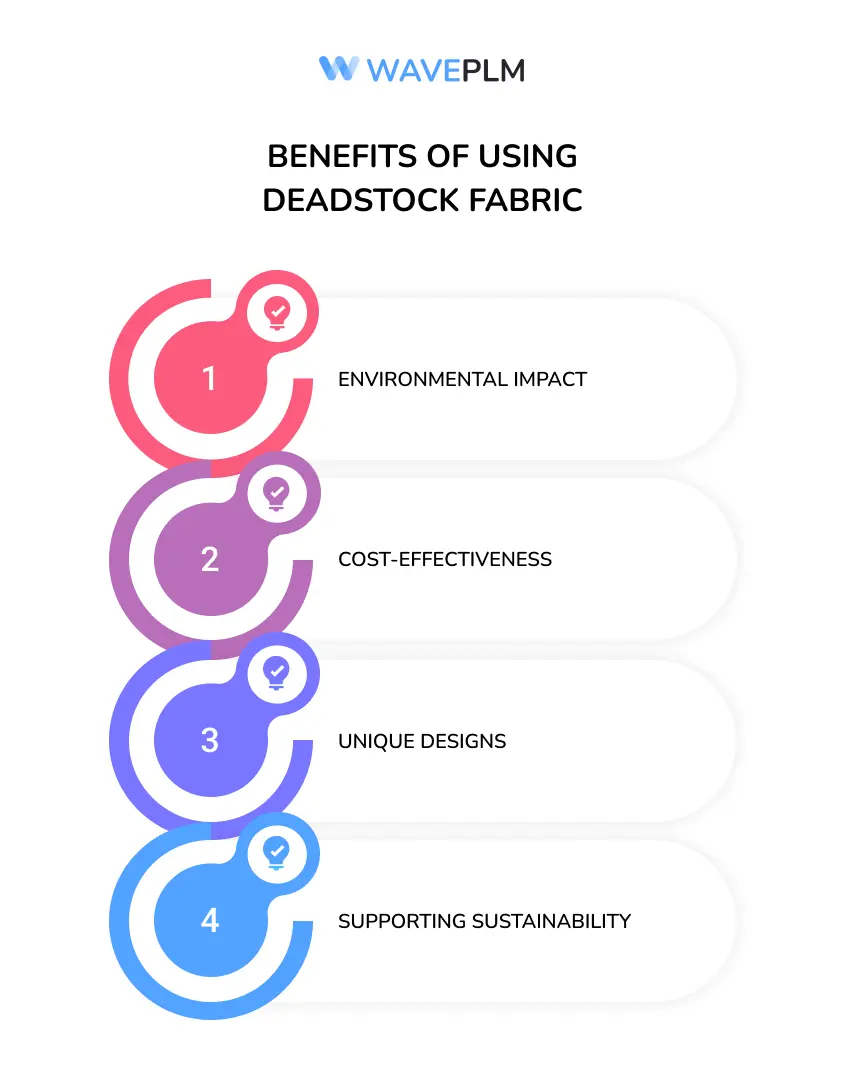
Benefits of Using Deadstock Fabric
- Environmental Impact: Utilizing deadstock fabric helps reduce the environmental footprint of the fashion industry. By using these materials again, we reduce the need for new fabric. This helps save resources and decreases pollution, including carbon and greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing production helps to use less water, energy, and chemicals in making textiles, which helps the environment.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For designers and manufacturers, deadstock fabric is often available at a lower cost than new fabric. This cost savings can be particularly beneficial for smaller brands and emerging designers who operate on tight budgets. Additionally, the reduced expense allows for more investment in sustainable practices and ethical labor practices, further enhancing a brand’s commitment to sustainability.
- Unique Designs: Deadstock fabrics often come in limited quantities, offering designers the opportunity to create unique, limited-edition pieces. This exclusivity can be a significant selling point for consumers looking for distinctive fashion items. Limited runs also add a sense of urgency for consumers, driving faster purchase decisions and reducing the likelihood of overproduction.
- Supporting Sustainability: Incorporating deadstock fabric into collections aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable and ethical fashion. Brands that prioritize sustainability can build a loyal customer base and enhance their reputation. Brands are teaching consumers to reduce waste and make eco-friendly choices by using deadstock fabrics.
Case Study: IWASASARI.COM As A Perfect Example Of Deadstock Fabric Use
One exemplary brand that has successfully integrated deadstock fabric into its collections is I was a Sari. This brand distinguishes itself by creatively upcycling preloved saris into a variety of products, showcasing a strong commitment to sustainability and unique design aesthetics.
Best Practices
I was a Sari sources its deadstock fabrics from local markets in India, where surplus materials from the sari industry are abundant. By repurposing these vibrant, high-quality fabrics, the brand reduces textile waste while preserving the rich cultural heritage of traditional Indian textiles.
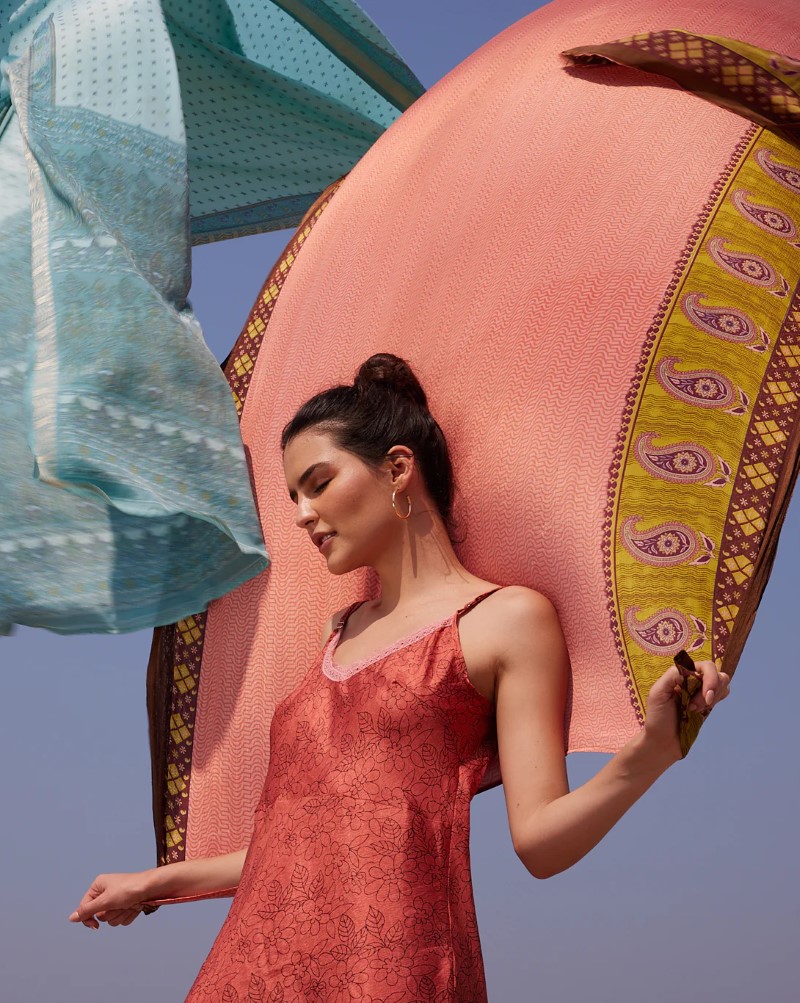

The brand employs a meticulous selection process to ensure the quality and authenticity of the fabrics. Each piece of fabric is carefully chosen for its durability and aesthetic appeal, ensuring that the final products are not only sustainable but also beautiful and unique.
Amazing Design
I was a Sari transforms deadstock fabrics into contemporary fashion items, blending traditional Indian textiles with modern design sensibilities. Their collections include a range of products such as bags, accessories, clothing, and home decor, all characterized by their vibrant colors, intricate patterns, and unique textures.
The brand’s design philosophy emphasizes creativity and innovation. By reimagining how traditional fabrics can be used, I was a Sari creates products that are both fashionable and sustainable. Their product designs appeal to a global audience, bridging the gap between traditional craftsmanship and contemporary fashion.
Social Impact
In addition to its environmental benefits, I was a Sari has a significant social impact. The brand employs women from underprivileged communities in Mumbai, providing them with training, fair wages, and a supportive work environment. This empowerment initiative not only enhances the women’s economic prospects but also fosters a sense of community and pride in their work.
The brand’s commitment to social responsibility is evident in its business model, which prioritizes ethical practices and community development. By focusing on both environmental and social sustainability, I was a Sari sets a benchmark for other brands in the industry.
The Problem of Fashion Waste
Fashion waste is a significant global issue, with millions of tons of textile waste generated each year. This waste accumulates at various stages of the fashion lifecycle, from production to consumer disposal. Key contributors to fashion waste include:
- Overproduction: Fast fashion brands often produce more garments than they can sell, leading to excess inventory that eventually becomes waste. This overproduction is driven by a business model that prioritizes rapid turnover and constant newness, resulting in large quantities of unsold stock.
- Consumer Behavior: The trend of fast fashion encourages consumers to purchase and discard clothing frequently, contributing to a throwaway culture. The availability of cheap, trendy garments leads to impulsive buying and a lack of consideration for the long-term value or durability of clothing.
- Manufacturing Waste: During the production process, fabric scraps and offcuts are often discarded, adding to the overall waste. Inefficient cutting techniques and poor planning can lead to significant amounts of unused fabric being thrown away.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Many garments end up in landfills when they are no longer wanted, as recycling and repurposing options are limited. The lack of infrastructure for textile recycling and the mixed-material composition of many garments make it difficult to divert textiles from landfills.
The Role of PLM Software in Waste Reduction
PLM software is important for managing a product throughout its entire lifecycle, from design to disposal. In fashion, PLM software helps reduce waste by improving different parts of the production process.
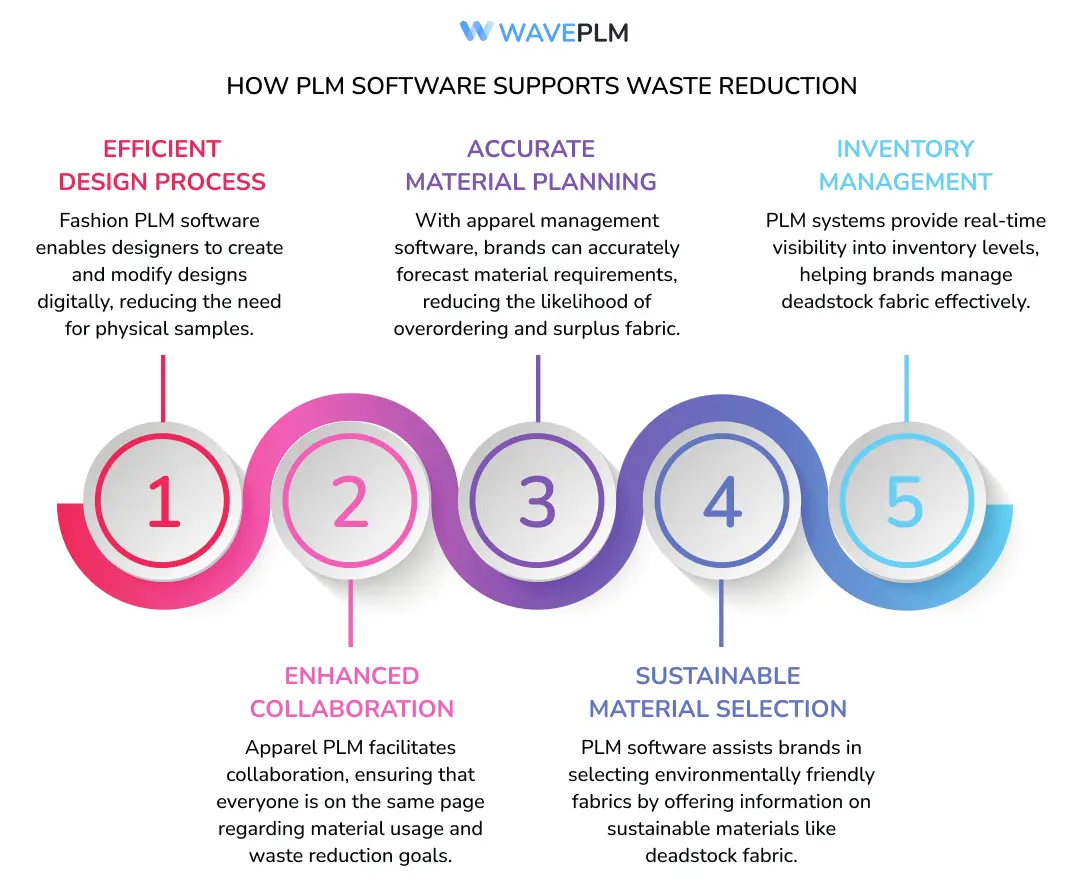
How PLM Software Supports Waste Reduction
- Efficient Design Process: Fashion PLM software enables designers to create and modify designs digitally, reducing the need for physical samples and prototypes. This minimizes fabric waste during the design phase. Digital tools also allow for better visualization and iteration, leading to more precise designs and fewer errors.
- Accurate Material Planning: With apparel management software, brands can accurately forecast material requirements, reducing the likelihood of overordering and surplus fabric. This precise planning helps in aligning production with actual demand, thereby minimizing excess inventory and associated waste.
- Inventory Management: PLM systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, helping brands manage deadstock fabric effectively. This ensures that surplus materials are utilized before new fabric is ordered, reducing the accumulation of unused materials.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Apparel PLM facilitates collaboration between designers, manufacturers, and suppliers, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding material usage and waste reduction goals. Improved communication and coordination lead to more efficient processes and a shared commitment to sustainability.
- Sustainable Material Selection: PLM software assists brands in selecting environmentally friendly fabrics by offering information on sustainable materials like deadstock fabric. This data helps brands make informed decisions. This integration promotes the shift towards a circular economy, where companies continually reuse and repurpose materials.
Challenges and Considerations
While deadstock fabric offers numerous benefits, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Limited Availability: Deadstock fabrics are often available in limited quantities, making it challenging to produce large-scale collections. Brands need to be creative in designing smaller, exclusive lines. This limitation requires strategic planning and flexibility in design and production.
- Quality control can be difficult when dealing with deadstock fabric. This is because the materials may vary in condition and characteristics. Ensuring consistency in quality can be a challenge. Brands must implement rigorous quality control measures to maintain high standards and customer satisfaction.
- Sourcing Challenges: Finding reliable sources of deadstock fabric requires effort and network building. Brands may need to establish relationships with multiple suppliers to maintain a steady supply. Building a network of trusted suppliers is crucial for ensuring the availability and quality of deadstock materials.
- Consumer Perception: Educating consumers about the value of deadstock fabric and sustainable fashion is crucial. Brands must effectively communicate the environmental benefits and unique qualities of their products. Clear messaging and marketing strategies can help shift consumer attitudes towards appreciating and valuing sustainable fashion.
The Role of Technology
Advancements in technology, including fashion PLM software, are driving the transition to sustainable fashion. These technologies enable brands to optimize their processes, reduce waste, and make data-driven decisions about material use. The integration of digital tools and sustainable practices is essential for creating a more responsible and environmentally friendly fashion industry.
Conclusion
Deadstock fabric plays a crucial role in reducing fashion waste and promoting sustainable practices within the industry. By repurposing surplus materials, brands can minimize their environmental impact, reduce costs, and create unique, eco-friendly designs. The integration of PLM software further enhances sustainability goals by streamlining processes and improving material management.
Fashion industry must use sustainable materials and new technologies to create a more responsible and eco-friendly future. Brands that prioritize sustainability and utilize leftover fabric can benefit the environment. They can also meet the growing demand for ethical fashion from socially responsible consumers.





Leave a Reply