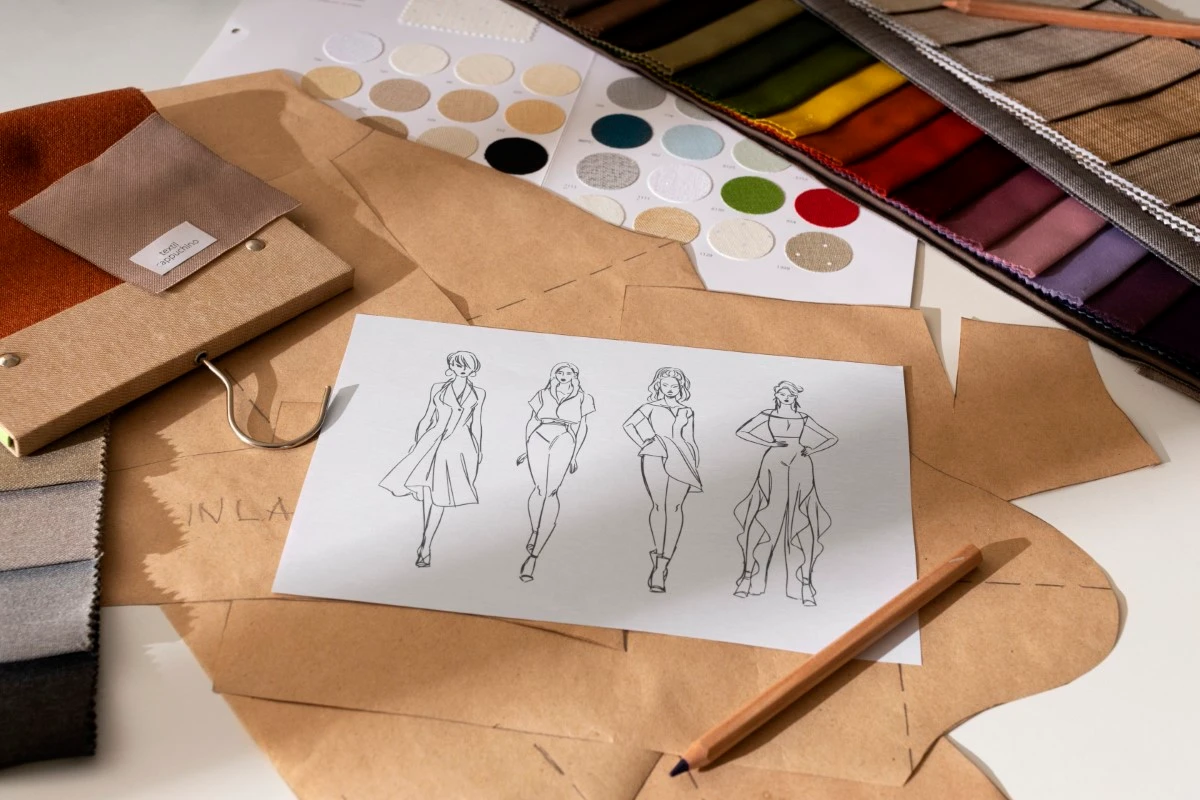

What is garment design? It is both an art and a science. Clothing design is a fundamental aspect of fashion, shaping the form, structure, and visual impact of garments through creative and technical decisions. It involves creating clothing that blends creativity, technical expertise, and market insight. In the fashion industry, the process transforms an initial concept into a high quality final product through a sequence of well-defined stages. This comprehensive guide expands on every step, discusses tools and skills, and shows how fashion PLM software supports the entire apparel lifecycle management.
The Meaning of Garment Design
Garment design merges aesthetics, comfort, and functionality with technical and production knowledge. It demands a clear understanding of the human body, fashion trends, and market demands. Designers must harmonize design elements, select the right fabric, and align with the brand’s target audience.
The process includes designing a garment from scratch, refining it with pattern making and fabric selection, and moving it through the construction process to completion. Designers work by combining creative methods, technical skills, and thoughtful decision-making to translate their ideas into finished products.
Three Main Aspects of Designing a Garment
- Creative Vision – Involving fashion illustration, color palettes, silhouettes, and intricate details that make designs unique. Visual interest is created through the use of lines, patterns, color, and texture, which enhances the aesthetic appeal of a garment and guides the viewer’s eye to define its shape or achieve desired effects.
- Technical Accuracy – Using paper templates, precise measurements, french curve, and tracing wheel to ensure the intended design matches production requirements.
- Production Practicality – Selecting cost-effective yet quality materials, streamlining the production process, and ensuring designs can be manufactured efficiently.

The Importance of Fabric
Fabric selection is one of the most important aspects of garment design, as it directly influences the look, feel, and performance of the final product. Fashion designers must have a clear understanding of how different fabrics behave, taking into account factors such as texture, weight, drape, and even sustainability. The right fabric can elevate a design, ensuring that the garment not only looks stylish but also functions as intended. For example, woven fabrics like cotton and denim are often chosen for their durability and structure in everyday wear, while stretch fabrics such as spandex or jersey are ideal for activewear and garments that require flexibility. Staying informed about the latest fabric innovations and fashion trends allows designers to make informed choices that set their creations apart in the competitive fashion industry. Ultimately, thoughtful fabric selection is essential to creating garments that resonate with consumers and stand the test of time.
Construction Techniques in Garment Design
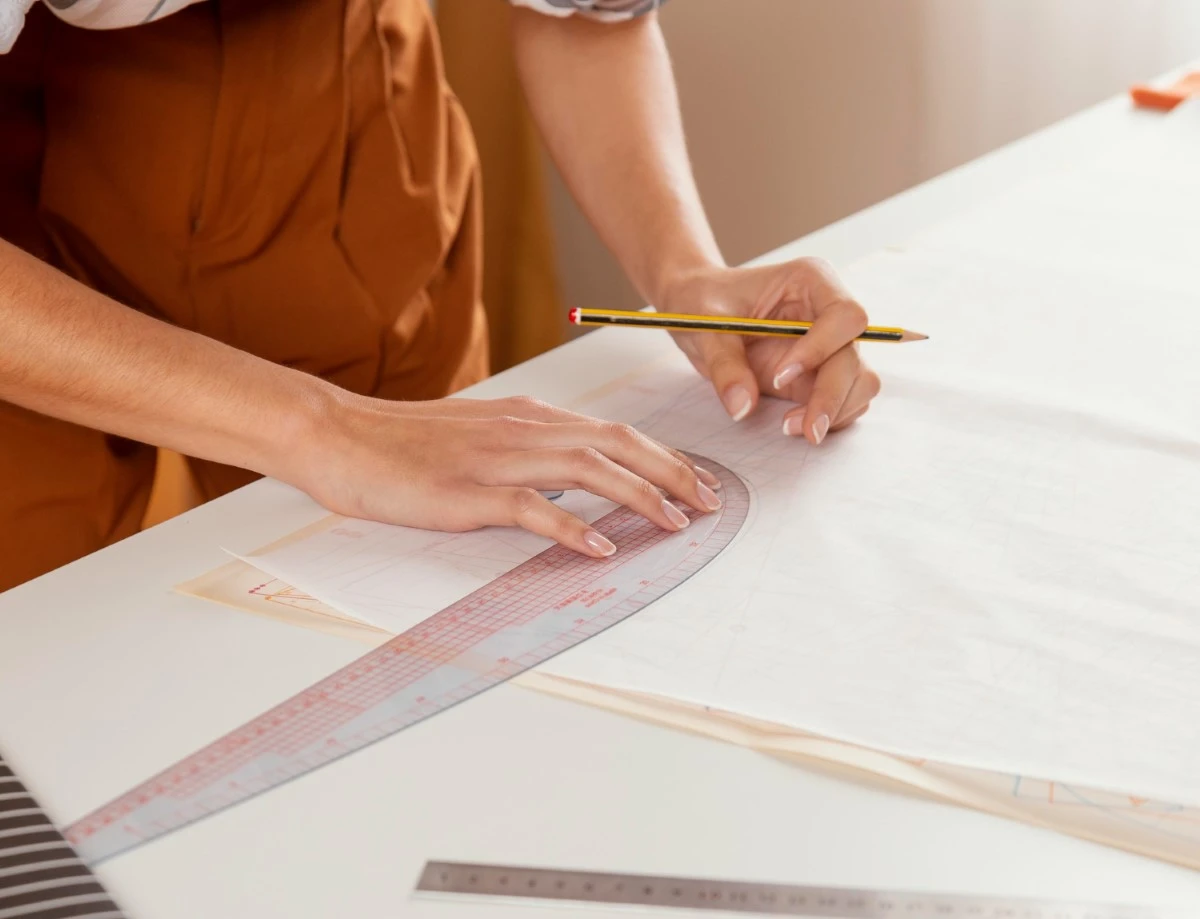
Mastering construction techniques is essential for fashion designers aiming to bring their creative visions to life. The construction process transforms flat fabric into a three-dimensional garment, requiring a blend of technical skill and artistic judgment. Designers must be proficient in sewing, draping, and pattern making, using tools like the sewing machine and dress form to achieve the desired shape and fit. Attention to seam lines, grain lines, and fabric grain ensures that each garment is both comfortable and durable.
Technical designers often collaborate closely with the design team to refine construction methods, ensuring that the finished garment meets both aesthetic and quality standards. For instance, using a serger sewing machine can create clean, professional seams that prevent fraying, while careful draping on a dress form allows for custom fits and intricate details. By honing their construction techniques, designers can create garments that are not only visually appealing but also built to last.
Pattern Making and Grading
Pattern making and grading are foundational steps in the garment design process, enabling fashion designers to translate their ideas into wearable clothing. Pattern making involves creating a paper pattern or digital template that serves as the blueprint for cutting fabric pieces. Techniques such as flat pattern making and draping help designers achieve the intended silhouette and fit. Tools like the french curve and tracing wheel are essential for adding smooth curves and transferring markings accurately.
Grading takes the process a step further by adjusting the original pattern to fit a range of sizes, ensuring that the garment flatters different body types and meets market demands. By following a comprehensive guide to pattern making and grading, designers can stay on trend and produce garments that appeal to a broad audience. For example, a designer might use a tracing wheel to mark seam allowances or a french curve to perfect the neckline, ensuring consistency and precision across all sizes.

The Apparel Design Process: Step-by-Step
|
Step |
Stage Name |
Key Activities |
Tools & Techniques |
PLM Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Concept Development |
Study fashion magazines, observe street style, research fashion trends |
Mood boards, fashion illustration |
Stores and shares visual references |
|
2 |
Sketching & Fashion Illustration |
Draw design details, test design elements, review with team, focus on detail in design elements and construction techniques to enhance the garment |
Digital design tools, sketchpads |
Version control for sketches |
|
3 |
Fabric Selection |
Compare woven fabrics, stretch fabrics, or expensive fabric for suitability |
Fabric swatches, supplier info |
Links fabrics to style records |
|
4 |
Pattern Making |
Draft paper pattern, digitize patterns for reuse; once the base pattern is created, it can be adjusted for multiple sizes or styles |
French curve, rulers, pinking shears |
Stores patterns in one system |
|
5 |
Sample Creation |
Build prototypes with sewing machine, check on dress form; sewing, seams, darts, added fullness—one example of handling seam allowances is using a turnback hem or mitered corner |
Sewing, seams, darts, added fullness |
Tracks fit changes and sample notes |
|
6 |
Pre Production & Final Approval |
Conduct quality control, approve final product specs |
Checklists, spec sheets |
Keeps records of approvals and changes |
Tools of the Technical Designer
A technical designer uses specialized tools to ensure accuracy:
- French curve for smooth shaping
- Tracing wheel to transfer pattern markings
- Pinking shears to reduce fraying on fabrics
- Dress form to visualize shape on the human body
- Sewing machine for assembling prototypes
The Value of Fashion Illustration
Fashion illustration is a powerful tool in the design process, allowing fashion designers to express their creative ideas and communicate them clearly to others. Through illustration, designers can visualize the mood, silhouette, and intricate details of a garment before it moves into production. A well-executed fashion illustration captures the essence of the design, making it easier for the development team to understand and execute the designer’s vision.
In the fast-paced fashion industry, the ability to create compelling illustrations gives designers a competitive edge, helping them pitch ideas to clients, collaborate with other designers, and guide the creation of technical packages. Whether sketching a concept for a new collection or developing detailed drawings for production, fashion illustration remains an essential skill for anyone involved in garment design.
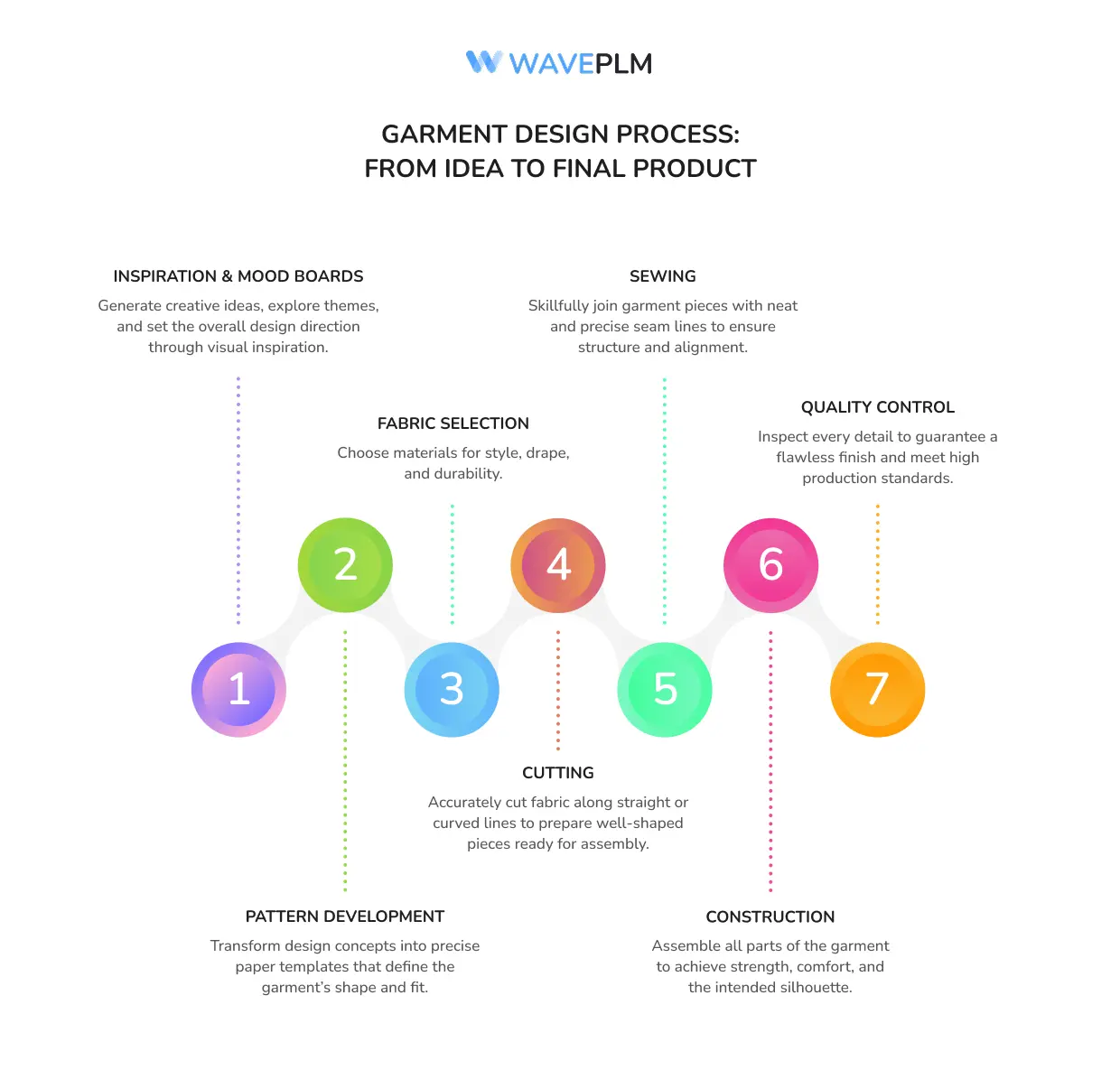
From Idea to Final Product
The journey from concept to final product is detailed and often time consuming:
- Designing a garment begins with inspiration and mood boards.
- Patterns are developed to form the desired shape.
- Fabric selection ensures the right fabric is chosen for drape, durability, and style.
- Cutting along straight lines or curves prepares pieces for assembly.
- Sewing joins pieces with precise seam lines.
- The construction process ensures strength and comfort.
- Quality control guarantees a high quality final product.
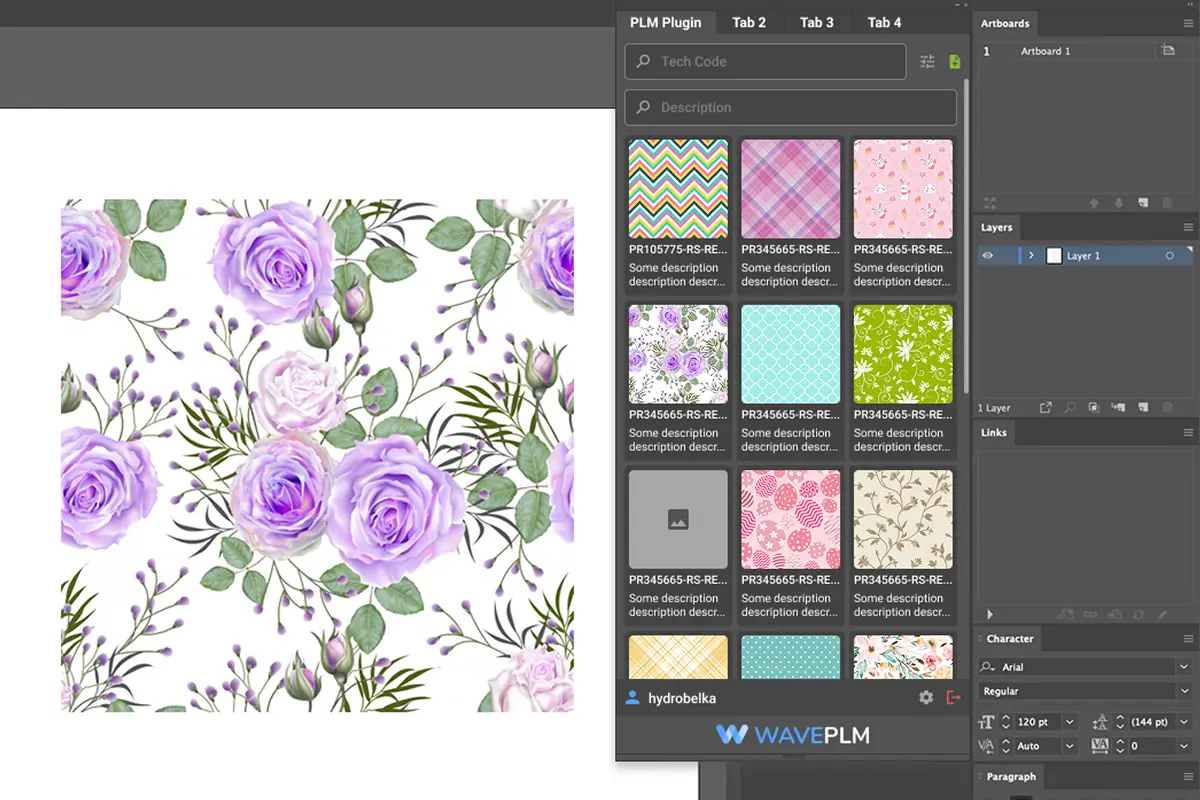
How Fashion PLM Software Fits In
Fashion PLM software enhances the design process by:
- Centralizing materials, sketches, and patterns
- Managing communication between designers, production, and suppliers
- Automating updates to reduce errors
- Supporting pre production planning
It enables fashion designers and other designers to collaborate efficiently, keeping the final design aligned with brand goals.
Sustainability in Fashion Design
Sustainability has become a central focus in the fashion industry, and fashion designers are increasingly expected to incorporate responsible practices into their garment design process. This means considering the environmental and social impact of every stage, from fabric selection to the production process. Designers can make a difference by choosing eco-friendly materials, such as organic cotton or recycled fabrics, and by minimizing waste through efficient pattern layouts and zero-waste techniques. Implementing sustainable production processes not only reduces the environmental footprint but also appeals to a growing segment of conscious consumers.
For example, a designer might opt for biodegradable fabrics or partner with suppliers who prioritize ethical labor practices. By embracing sustainability, designers can create garments that are both fashionable and responsible, ensuring their work contributes to a more sustainable future for the fashion industry. As sustainability continues to shape market demands, designers who prioritize these values will be well-positioned to lead the industry forward.
Quick Garment Design Checklist
|
Stage |
Tasks |
Done |
|
Concept |
Research, build mood board |
☐ |
|
Sketch |
Create, refine, review |
☐ |
|
Fabric |
Source, approve, match to patterns |
☐ |
|
Pattern |
Draft, digitize, adjust |
☐ |
|
Sample |
Assemble, fit test, adjust |
☐ |
|
Pre Production |
QC, approve, document |
☐ |
Becoming a Garment Designer
To become a garment designer, you need training in fashion design, pattern making, and garment making techniques. Gaining hands-on experience with sewing, fabric selection, and design elements is essential. Networking with fashion brands, staying updated through fashion magazines, and practicing fashion illustration will help you stay on trend.
Final Thoughts
Mastering the garment design process requires dedication, technical skill, and creative flair. Whether you are exploring how to design clothes or improving existing garment designing skills, each step plays a role in achieving a high quality final product. With fashion PLM software, designers can streamline workflows, respond quickly to market demands, and produce garments that combine creativity with efficiency—meeting the needs of both mass market and premium fashion brands.





Leave a Reply