Fashion brands face growing pressure to meet regulatory compliance standards for safety, labeling, sustainability, and ethical practices. Governments, consumers, and organizations such as the federal trade commission expect companies to ensure compliance with strict safety standards, labeling requirements, and environmental guidelines.
For many businesses in the fashion industry, staying ahead of these evolving regulations feels increasingly complex. The good news is that PLM software provides a structured way to simplify regulatory compliance management. By centralizing data, tracking compliance requirements, and ensuring supply chain transparency, apparel PLM helps brands protect consumers, build trust, and mitigate risks of non compliance.
This article explains what regulatory compliance means for the fashion industry, how PLM software supports compliance frameworks, and why aligning business processes with regulations creates long-term success.
What Does Regulatory Compliance Mean in Fashion?
Regulatory compliance means following laws, standards, and guidelines designed to protect consumers, workers, and the environment. In the apparel and textile industry, regulatory requirements cover areas such as product compliance, labeling requirements, ethical practices, and environmental impact. Non compliance can result in financial penalties, restricted market access, loss of consumer trust, or reputational damage that can take years to repair.
Fashion regulations apply to a wide range of product categories, including textile products, children’s products, and consumer goods. For example:
- Safety standards demand testing for toxic substances in raw materials.
- Labelling requirements require accurate fiber content, care instructions, and country of origin labeling.
- Ethical practices demand occupational health and safe working conditions for employees in manufacturing processes.
- Environmental regulations require companies to reduce packaging waste and track restricted substances.
The goal of regulatory compliance is not only to comply with local and international laws but also to protect consumers and support public interest by enforcing standards across the supply chain.
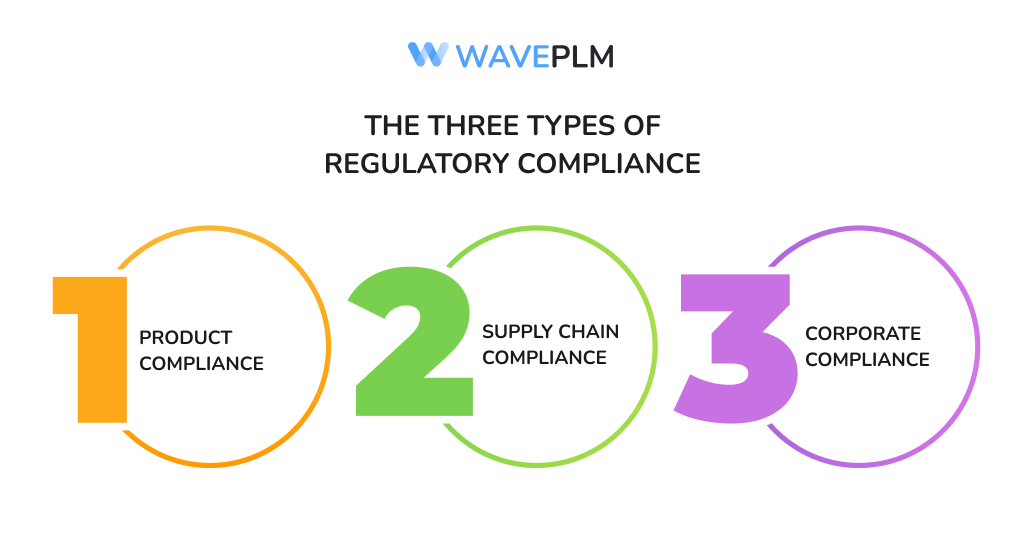
The Three Types of Regulatory Compliance
In fashion, regulatory compliance is often categorized into three types:
- Product compliance: ensuring that textile materials and finished goods meet safety standards and restricted substance requirements.
- Supply chain compliance: monitoring ethical practices, labor conditions, and supplier audits to ensure transparency across different countries.
- Corporate compliance: aligning internal business processes with regulations such as general data protection regulation (GDPR), occupational health standards, and safety administration requirements.
By covering these three areas, companies meet safety standards, avoid potential hazards, and ensure transparency from raw materials to the final product.
Why Apparel Compliance Is Essential
Apparel compliance ensures brands operate responsibly. Some key areas include:
- Product compliance: testing raw materials and textile materials for toxic substances or potential risks.
- Labelling requirements: providing accurate fiber content, care instructions, and country of origin details.
- Ethical practices: enforcing standards for occupational health, safe working conditions, and fair wages.
- Environmental impact: reducing packaging waste, measuring sustainability goals, and controlling emissions.
By following fashion regulations, companies protect consumers, educate employees about compliance frameworks, and demonstrate ethical practices. Strong apparel compliance also helps companies secure market access in the European Union’s regulated markets and other regions where national authorities enforce strict laws.
How PLM Software Simplifies Compliance
PLM software (Product Lifecycle Management) manages product specifications, regulatory information, and compliance activities across the production process. Unlike ERP systems, which focus on financial industry workflows, apparel PLM centers on product design, manufacturing processes, and supply chain compliance.
Key ways PLM software helps ensure compliance:
- Tracks regulatory requirements across different countries.
- Creates digital audit trails for regular audits by national authorities.
- Stores supplier audits, certifications, and compliance activities in one system.
- Links quality control directly with manufacturing processes.
- Provides real-time dashboards for supply chain transparency and greater transparency for stakeholders.
By embedding compliance frameworks into daily workflows, PLM transforms compliance from a separate task into a natural part of business.
Benefits of Using Apparel PLM for Regulatory Compliance
|
Benefit |
Impact on Business |
|---|---|
|
Centralized compliance data |
Faster approvals and fewer errors |
|
Automated quality control |
Fewer recalls and safer consumer products |
|
Supplier compliance tracking |
Stronger supply chain management and transparency |
|
Real-time reporting |
Better response to new laws and regulations |
|
Integrated workflows |
Reduced costs and improved business processes |
These benefits allow companies to comply with fashion regulations while delivering safer consumer products and informed choices to customers.
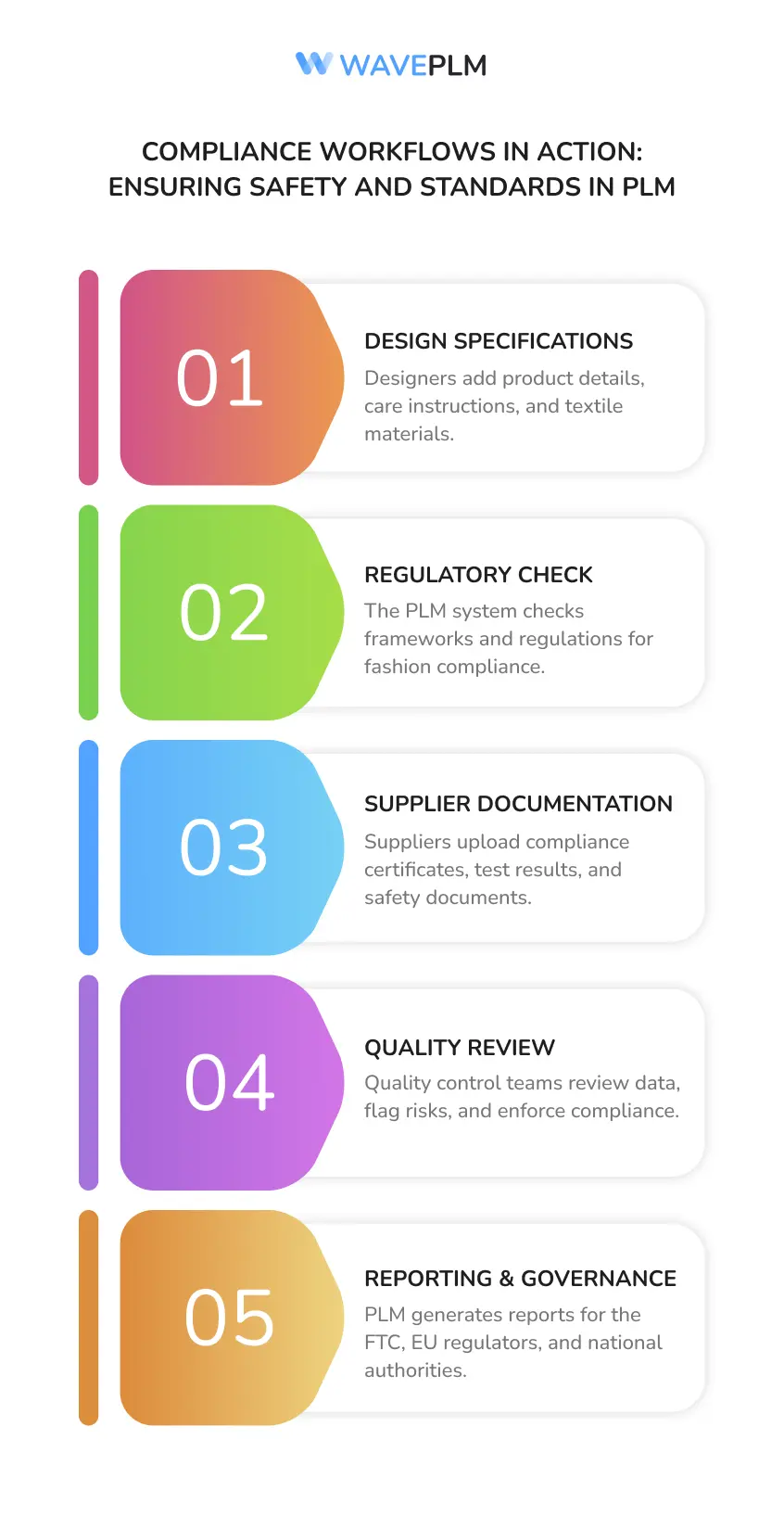
Compliance Workflows in Action
Here’s how regulatory compliance management looks in an apparel PLM system:
- Designers add product specifications, care instructions, and textile materials.
- PLM checks against compliance frameworks and regulatory information for fashion regulations.
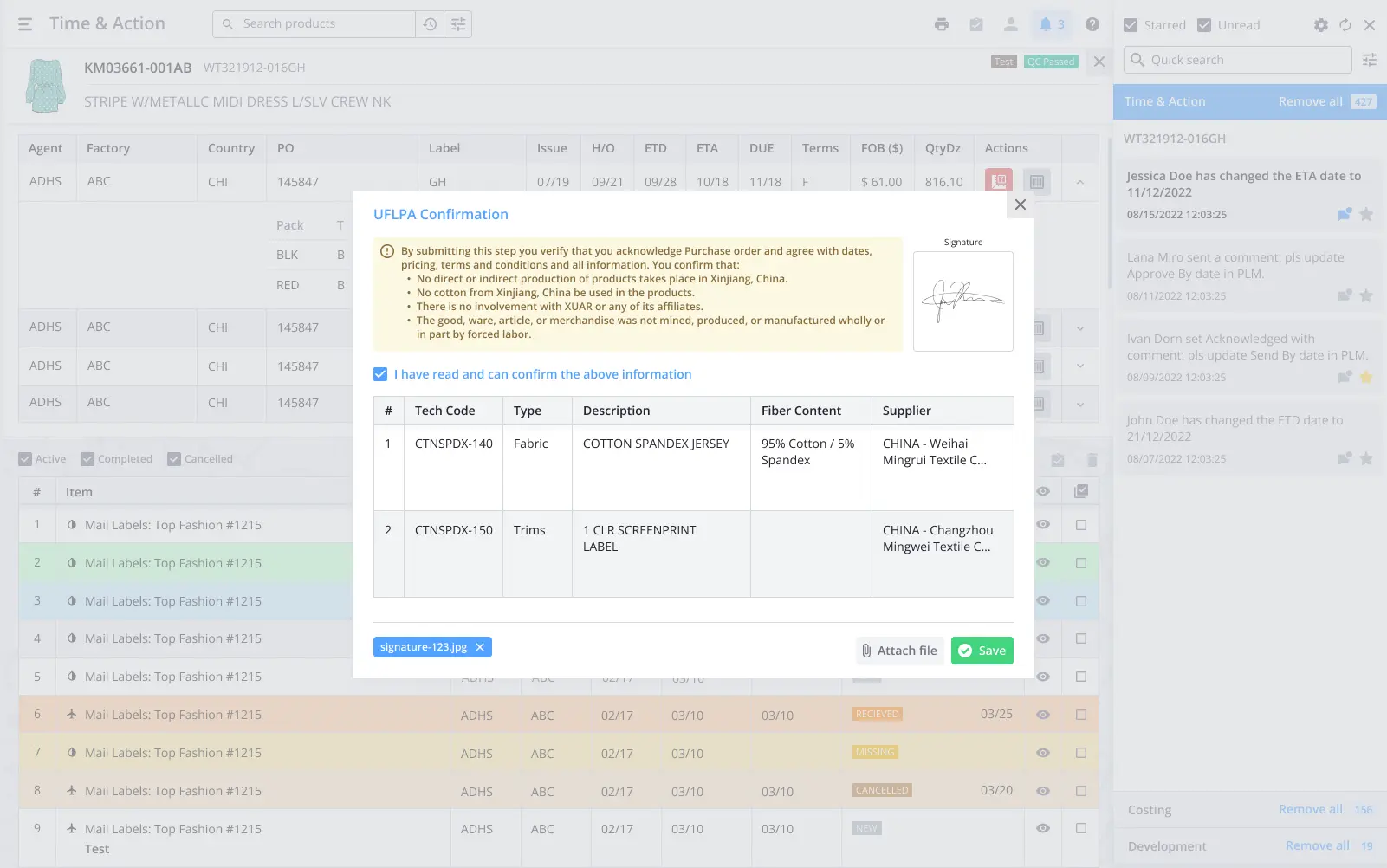
- Suppliers upload certificates, restricted substances test results, and children’s clothing safety reports.
- Quality control teams review results, flag potential hazards, and enforce standards.
- PLM generates compliance reports for the federal trade commission, European Union’s regulators, and national authorities.
This process ensures companies comply with safety standards, reduce potential risks, and keep consumer protection at the center of their operations.
Common Risks Without PLM Software
Brands that rely on spreadsheets, emails, or manual processes often face:
- Missing labeling requirements and regulatory information.
- Non compliance with occupational health or safety administration standards.
- Limited visibility into supplier audits and children’s products certifications.
- Delayed approvals that slow down the production process.
- Inability to enforce compliance requirements across global supply chains.
These issues increase potential risks, raise costs, and undermine consumer protection.
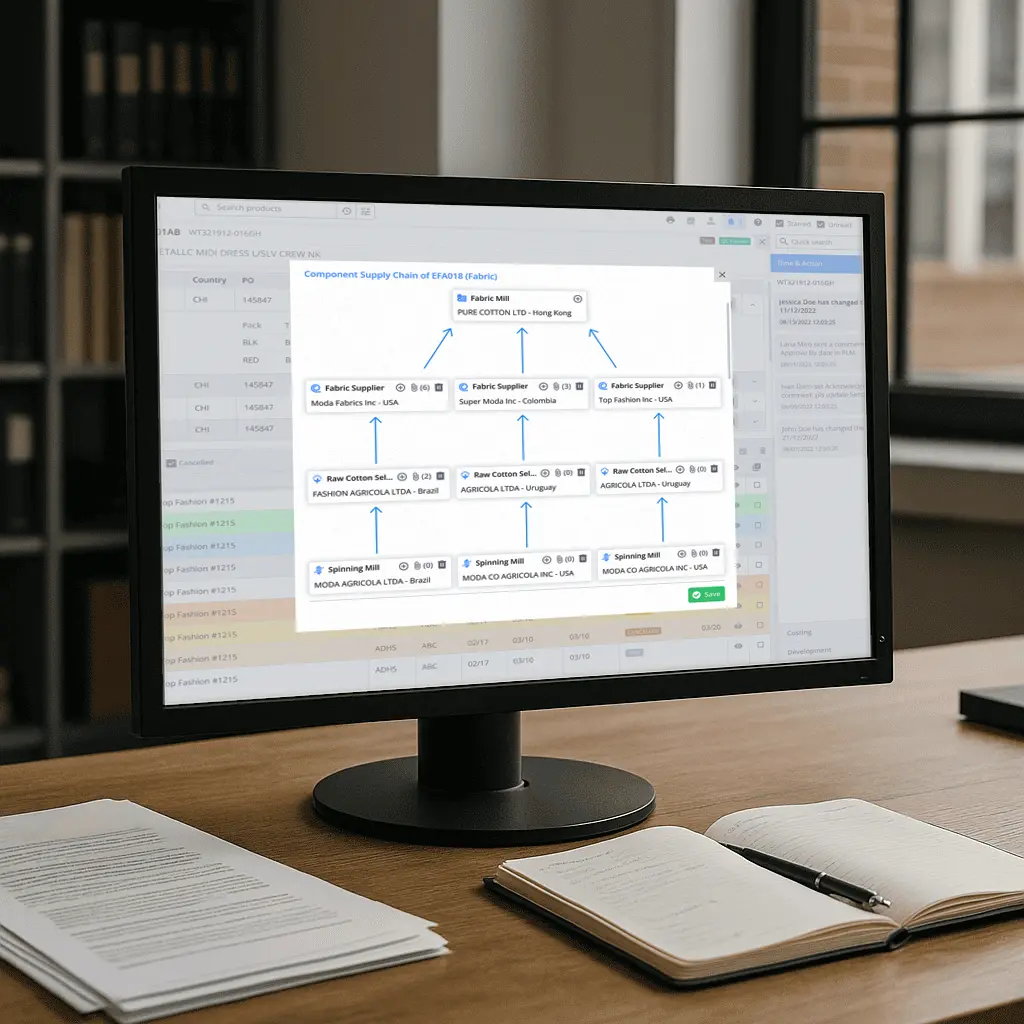
Strengthening Supply Chain Compliance
The fashion industry relies heavily on raw materials sourced worldwide. Supply chain compliance requires constant monitoring, supplier audits, and ensuring transparency in sourcing. PLM software provides tools to:
- Monitor supplier compliance activities in real time.
- Track labelling requirements, safety standards, and restricted substances.
- Record certifications for children’s clothing, consumer products, and other categories.
- Provide supply chain transparency to mitigate risks and meet safety standards.
By integrating supplier audits and enforcing standards, apparel PLM builds greater transparency into global supply chain management.
Linking Compliance and Quality Control
Compliance and quality control go hand in hand. Apparel PLM strengthens this link by focusing on resources such as the measurement sheet:
- Flagging failed safety standards or toxic substances during testing.
- Recording corrective actions and linking them to suppliers.
- Ensuring final product quality by integrating product compliance checks into the production process.
- Protecting consumers by addressing potential hazards before products reach the market.
This closed loop between compliance management and quality control ensures consumer protection while meeting fashion regulations.
How PLM Educates Employees and Supports Ethical Practices
Compliance is not only about systems but also people. Companies need to educate employees on compliance requirements, compliance frameworks, and ethical practices. Apparel PLM supports this by:
- Providing accessible compliance libraries.
- Enforcing standards through automated alerts and workflows.
- Ensuring transparency for different teams across business processes.
This approach creates a culture where compliance is part of daily work rather than a last-minute checklist.
The Future of Fashion Regulations
The regulatory landscape is evolving rapidly. Governments introduce new laws to address environmental impact, packaging waste, and data security. National authorities demand greater transparency, while consumers expect ethical practices and safer consumer products. Fashion brands must adapt to these changes to protect market access and remain competitive.
Future directions include:
- AI-driven compliance checks: predicting potential risks before production.
- Blockchain technology: securing supply chain transparency and protecting consumers.
- Sustainability dashboards: tracking carbon footprint and environmental impact of textile materials.
- Regular audits: making compliance a continuous process, not an annual event.
Brands that adopt PLM software gain an advantage by aligning with these future compliance frameworks.

Conclusion
In today’s fashion sector, regulatory compliance is more than following rules—it defines business success. Apparel compliance, product compliance, and supply chain compliance help companies meet safety standards, protect consumers, and demonstrate ethical practices. By embedding compliance activities into PLM software, companies reduce non-compliance risks, streamline business processes, and ensure compliance across different product categories.
PLM software transforms regulatory compliance management into a daily routine that supports consumer protection, mitigates risks, and secures global market access. As the regulatory landscape becomes increasingly complex, apparel PLM offers the tools to ensure compliance, improve supply chain transparency, and support sustainable growth in the fashion industry.





Leave a Reply