
Law of Supply and Demand in Economics
The law of supply and demand is a cornerstone of economic theory, describing the relationship between the availability of a product (supply) and the desire for that product (demand). These are the basic laws that govern economic interactions, shaping how prices and quantities are determined. This relationship is pivotal in determining the price of goods and services in a market economy, and these dynamics play out across various markets, where buyers and sellers interact under different market structures. When supply and demand are balanced, the market operates efficiently, and resources are optimally allocated.
Imbalances, however, lead to surpluses or shortages, necessitating adjustments in pricing and production. Understanding why demand important is crucial for making informed decisions about pricing, production levels, and market forecasting. This principle is particularly significant in the apparel industry, where trends and seasons greatly influence both clothing supply and demand. Let’s delve deeper into this concept, with a focus on the fashion sector and the role of supply chain management, demand forecasting, and innovations in maintaining supply chain resilience.
Introduction to Economics and the Law of Supply and Demand
The law of supply and demand is a foundational concept in economics that explains how market prices are set and how they influence the behavior of buyers and sellers. At its core, this law describes the relationship between the quantity of a product or service that suppliers are willing to sell (supply) and the quantity that buyers are willing to purchase (demand) at various prices. In any market, the law of supply and demand states that prices will adjust until the quantity supplied matches the quantity demanded. This balancing act helps determine not only the market prices for goods and services but also how much is produced and sold. For businesses, understanding how supply and demand interact is essential for setting prices, planning production, and responding to changes in consumer demand. Whether you are a supplier deciding how much to produce or a consumer deciding what to buy, the law of supply and demand shapes every transaction in the market.
Understanding Supply and Demand
Supply refers to the quantity of a product available for purchase at any given time. In the apparel industry, this includes the number of clothing items produced by designers and manufacturers. Factors that influence supply include production costs, availability of raw materials, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, and logistical considerations. For instance, a disruption in the supply chain of cotton can significantly affect the availability of cotton-based clothing.
Demand pertains to how much of a product consumers are willing to buy. In fashion, many things like trends, seasons, marketing, and the target market’s socio-economic status affect demand. For example, demand for winter coats rises as temperatures drop, and swimwear sees a peak in summer months. Understanding these demand planning patterns is crucial for effective supply chain planning. Demand levels fluctuate based on factors such as price changes, consumer income, and shifting preferences, which can lead to increases or decreases in demand depending on the situation.
The Demand Curve: Visualizing Consumer Behavior
The demand curve is a powerful tool for visualizing how consumers respond to different prices. Typically shown as a downward sloping line on a graph, the demand curve illustrates that as the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded by consumers falls, and vice versa. This relationship reflects the basic principle that consumers are more likely to buy a product when it is offered at a lower price. The demand curve can shift due to changes in consumer preferences, income levels, or the availability of substitute goods. For example, if a new trend makes a particular style of clothing more desirable, the entire demand curve for that item may shift to the right, indicating increased demand at every price point. By analyzing the demand curve, businesses can better understand how consumers make purchasing decisions and set pricing strategies that align with market demand.
The Law of Supply: How Producers Respond
The law of supply explains how producers react to changes in market prices. According to this principle, as the price of a product or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers also increases. This is because higher prices make it more profitable for suppliers to produce and sell additional units, covering their production costs and generating higher profits. Conversely, when prices fall, the quantity supplied tends to decrease, as producing the good becomes less attractive financially. The supply curve, which is typically upward sloping, visually represents this positive relationship between price and quantity supplied. Factors such as production costs, availability of raw materials, and advances in production technology can all influence the supply curve. For businesses, understanding the law of supply is crucial for determining how much to produce and at what price to offer their products in order to remain competitive and profitable.
The Interaction of Supply and Demand
The interplay between supply and demand determines market prices and the quantities of goods sold. Here’s a detailed look at how these dynamics work:
- Equilibrium: The point where supply equals demand is known as the equilibrium price. At this price, the quantity of apparel produced matches what consumers are willing to buy—consumers buy the quantity supplied at the market price. This is the point where the market clears and the market price is established. For instance, if a popular brand releases a limited-edition jacket, the equilibrium price is reached when the quantity produced aligns with consumer demand, ensuring no surplus or shortage.
When illustrating these relationships, supply curves and demand and supply curves are plotted on a graph. The horizontal axis represents quantity, while the vertical axis represents price. These curves help visualize how changes in supply or demand affect the market.
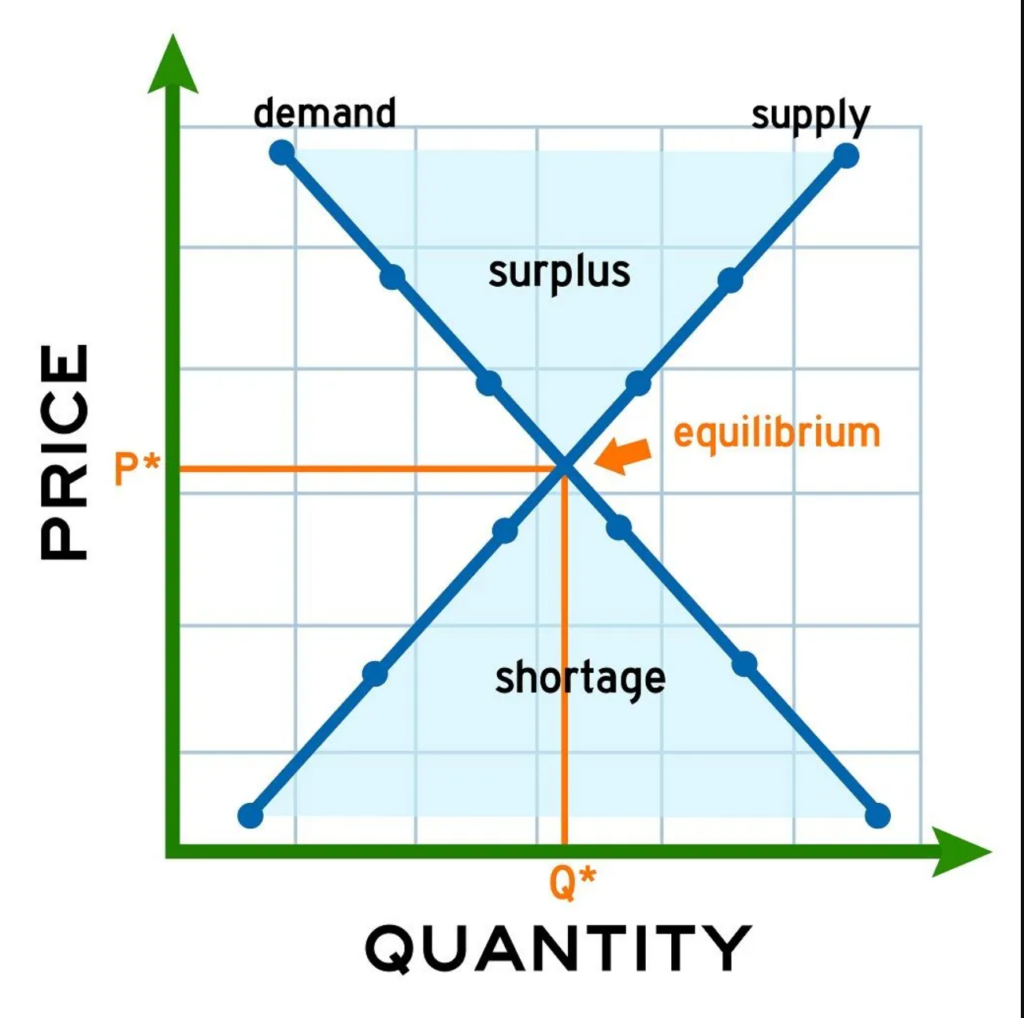
- Surplus and Shortage:
Here are some examples to illustrate surplus and shortage in real-world scenarios:
- Surplus occurs when supply exceeds demand, often leading to discount sales or clearance events to reduce excess inventory. For example, if a retailer overestimates the demand for summer dresses, it may end up with excess stock that needs to be sold at a lower price. If supply remains constant but demand decreases, lower prices or price drops may result as the market adjusts.
- Shortage happens when demand exceeds supply, driving prices up as consumers compete to purchase the limited items available. A fashion example could be a highly coveted designer handbag that sells out quickly, causing resale prices to skyrocket. If demand increases while supply remains constant, price rises or a higher price may occur.
Equilibrium Price: Where Supply Meets Demand
The equilibrium price is the point at which the supply and demand curves intersect, representing the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. At this market-clearing price, there is no surplus or shortage—every unit produced is sold, and every consumer who wants to buy at that price can do so. The equilibrium price is not fixed; it can change in response to shifts in consumer preferences, production costs, or other market factors. For example, if production costs rise due to more expensive raw materials, the supply curve may shift, leading to a new equilibrium price. Understanding how the equilibrium price is determined helps businesses set the right price for their products and anticipate how changes in the market will affect both supply and demand. Achieving market equilibrium ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that the market operates smoothly.
Price Elasticity: Measuring Sensitivity to Price Changes
Price elasticity is a key concept that measures how sensitive the quantity demanded or supplied is to changes in price. The price elasticity of demand indicates how much the quantity demanded will change in response to a price change, while the price elasticity of supply measures how much the quantity supplied will adjust. Products with high price elasticity see significant changes in demand or supply when prices fluctuate—luxury goods and non-essential items often fall into this category. In contrast, products with low price elasticity, such as basic necessities, experience smaller changes in quantity demanded or supplied when prices change. Understanding price elasticity helps businesses develop effective pricing strategies, forecast revenue, and respond to market shifts. By analyzing elasticity, companies can predict how consumers and suppliers will react to price changes and make informed decisions about production, inventory, and pricing.
Supply and Demand in the Fashion Industry
The fashion industry is highly sensitive to the dynamics of supply and demand due to its fast-paced nature and seasonal cycles. Here’s how these concepts apply in the apparel sector:
- Trends and Influences: Fashion trends heavily influence demand. When a celebrity is seen wearing a new style, it can create a sudden spike in demand. Brands may increase supply to meet this surge or risk losing sales to competitors. Additionally, high demand can attract new suppliers to enter the market, further increasing overall supply.
- Seasonal Changes: Demand for clothing varies with the seasons. Retailers need to forecast these changes accurately to adjust their supply. Winter coats have high demand in cold months, while swimwear peaks in summer.
- Production Lead Time: The time it takes to design, manufacture, and distribute clothing affects supply. Fast fashion brands excel by shortening lead times, allowing them to respond quickly to changing demands. However, supply constraints, such as material shortages or supply chain disruptions, can limit a brand’s ability to respond to demand.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management ensures that supply meets demand. When supply increases without a corresponding rise in demand, surpluses can occur, leading to excess inventory and potential markdowns. Fashion PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems help brands track trends, manage production schedules, and optimize stock levels to avoid surpluses and shortages in the global supply chain. These systems also help balance supply with demand, supporting better inventory control and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
The Role of Innovation in Fashion Supply and Demand
Innovation plays a significant role in shaping both supply and demand in the apparel industry. Advances in technology and new business models can profoundly affect how fashion products are produced, marketed, and consumed.
1. Technological Advancements:
- Automation and AI: The use of automation and artificial intelligence in manufacturing has streamlined production processes, reducing costs and lead times. This allows brands to increase their supply rapidly in response to rising demand. Automation also enables brands to efficiently produce each additional unit of clothing, making it easier to scale up production as needed. For example, automated cutting machines and AI-driven quality control systems can significantly boost production efficiency. Additionally, these technologies help reduce cost, making production more economically viable.
- Sustainable Technologies: Innovations in sustainable materials and eco-friendly production methods are reshaping the supply side of fashion. As consumer demand for sustainable fashion grows, brands are investing in technologies that reduce environmental impact, such as biodegradable fabrics and water-efficient dyeing processes.
2. Digital Platforms and E-commerce:
- Online Shopping: The rise of e-commerce has transformed how consumers purchase fashion items, increasing demand for convenient online shopping experiences. Brands are now able to reach a global audience, further influencing demand.
- Virtual Try-Ons and Sampling: Augmented reality (AR) and virtual try-on technologies enhance the online shopping experience, reducing return rates and boosting consumer confidence, thereby influencing demand.
3. Data Analytics and Personalization:
- Consumer Insights: Advanced data analytics tools help brands understand consumer behaviour and preferences, allowing for more accurate demand forecasting. By analyzing purchasing patterns, brands can adjust their supply strategies to better meet market demand. Understanding marginal utility also helps brands predict how likely consumers are to purchase additional items as their satisfaction with each extra product changes.
- Personalized Marketing: Personalization technologies enable brands to offer tailored product recommendations and marketing messages, enhancing consumer engagement and driving demand.
It is important to note that other factors, such as market conditions, supply chain issues, and government regulations, also influence supply and demand in the apparel industry.
Fashion PLM and Its Impact on Supply and Demand
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems are crucial tools in the fashion industry, helping brands manage the entire lifecycle of a product from initial concept through design, production, and retail. Here’s how PLM can become a competitive advantage in supply chain processes:
1. Streamlining Product Development:
- Efficient Design Processes: PLM systems facilitate collaboration among design teams, ensuring that product concepts are developed efficiently. This reduces time-to-market and helps brands respond quickly to emerging trends, aligning supply with demand. In markets approaching perfect competition, where many brands offer similar products, PLM helps brands stay competitive by enabling rapid innovation and efficient processes.
- Material Management: Brands can optimize their supply chain by managing raw materials and components in the PLM system. This helps reduce waste and ensures that necessary materials are always available.
2. Enhancing Production Planning:
- Forecast Accuracy: PLM systems integrate with demand forecasting tools, providing accurate predictions of future sales. This enables brands to plan their production schedules more effectively, aligning supply with anticipated demand.
- Quality Control: PLM systems help maintain high-quality standards by managing quality control processes throughout the production cycle. Consistent product quality can enhance brand reputation and drive consumer demand.
- Pricing Strategy: PLM systems also help brands set prices based on real-time data, allowing for dynamic pricing strategies that reflect current market conditions and demand.
3. Optimizing Inventory Management:
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: PLM systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, helping brands manage stock more efficiently. A classic example is when PLM prevents overproduction of a seasonal item, avoiding surplus inventory, or helps avoid shortages of a high-demand product during peak season.
- Demand-Driven Supply Chains: Brands can improve inventory management by aligning supply chain operations with real-time demand data. This helps them meet consumer needs more accurately and efficiently. Matching supply chain operations with current demand data allows brands to better manage their inventory. This ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and increased efficiency.
By optimizing supply chain processes with PLM, brands can gain market power, enabling them to influence market outcomes and strengthen their competitive position.
Supply Chain Resilience in the Apparel Industry
Supply chain resilience refers to the ability of a supply chain to anticipate, prepare for, and respond to disruptions. In the apparel industry, where trends and consumer demands are constantly evolving, maintaining supply chain resilience is critical.
1. Risk Management:
- Diversified Sourcing: To mitigate risks associated with single-source dependencies, apparel brands often diversify their sourcing strategies. This includes working with multiple suppliers across different regions to reduce vulnerability to local disruptions.
- Contingency Planning: Developing contingency plans for potential disruptions, such as natural disasters or political instability, helps brands maintain supply chain performance. This includes identifying alternative suppliers and logistics providers.
- When demand decreases due to disruptions, brands must quickly adapt their strategies to avoid excess inventory and financial losses.
- Supply chain disruptions can also cause prices rise, as limited supply or increased costs are passed on to consumers.
2. Technology Integration:
- Supply Chain Visibility: Using IoT and blockchain can improve supply chain visibility, helping brands monitor products from start V-ing finish. This visibility helps in identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate.
- Collaborative Platforms: Utilizing collaborative platforms that connect all stakeholders in the supply chain enhances communication and coordination, improving overall supply chain resilience.
- Brands use demand and supply curves to forecast and respond to market changes, allowing them to better align production and inventory with expected demand.
- Flexible Manufacturing: Investing in flexible manufacturing systems allows brands to quickly adjust production volumes and switch between different product lines as demand shifts.
- Responsive Logistics: A flexible logistics network helps brands adapt to changes in consumer demand and market conditions. This ensures that supply chain performance remains strong, even during disruptions.
- Disruptions can result in fewer people buying products, which impacts overall sales and inventory management.
- When overstock occurs or demand decreases, price drops may be necessary to clear excess inventory and maintain cash flow.
Practical Example: Supply and Demand in Clothing
Consider a fashion brand launching a new line of eco-friendly sneakers:
- Initial Demand: The brand uses social media influencers and targeted marketing campaigns to create buzz around the new product, generating high initial demand.
- Production Planning: Using PLM systems, the brand efficiently manages the design and manufacturing processes, ensuring that the sneakers are produced with sustainable materials and methods. The brand also evaluates whether to produce an additional unit based on real-time demand forecasts to optimize production and avoid excess inventory.
- Inventory Management: The brand tracks inventory levels in real-time using its PLM system, ensuring that supply meets the anticipated demand without overproducing. The brand monitors different supply states and works to balance supply with demand, making adjustments as needed to prevent stockouts or surplus.
- Pricing Strategy: The brand sets an initial price based on production costs and expected demand. If demand exceeds supply, the brand might consider a restock or a price adjustment to manage consumer expectations.
- Consumer Feedback: By analyzing sales data and consumer feedback, the brand gains insights into market preferences, which can inform future product development and marketing strategies. The brand also reviews supply curves to better understand how changes in price and demand affect supply decisions for upcoming releases.
Demand Forecasting in Supply Chain Management
Accurate demand forecasting is critical for maintaining an efficient supply chain. In the apparel industry, where trends can change rapidly, precise demand forecasting helps brands align their supply with market demand, reducing the risk of surpluses and shortages. Understanding why demand is important allows businesses to optimize supply chain efficiency, set appropriate inventory levels, and respond quickly to market changes.
1. Historical Data Analysis: Analyzing historical sales data helps brands identify patterns and trends that can inform future demand forecasts. Examining demand levels over time enables more accurate predictions and helps improve forecasting models. This includes understanding seasonal variations and the impact of marketing campaigns.
2. Predictive Analytics: Leveraging predictive analytics tools enables brands to anticipate future demand based on various factors, such as current trends, economic indicators, and consumer sentiment. These tools also consider other factors like supply chain disruptions and government regulations, using advanced algorithms to generate accurate forecasts.
3. Market Research: Conducting market research, including surveys and focus groups, provides valuable insights into consumer preferences and potential demand shifts. Brands study different markets and market structures to anticipate changes in demand and adapt their strategies accordingly. This information helps brands make informed decisions about product development and inventory management.
4. Real-Time Data Integration: Integrating real-time data from various sources, such as sales channels, social media, and market reports, enhances the accuracy of demand forecasts. This real-time data provides a dynamic view of market conditions, allowing brands to adjust their supply chain strategies accordingly.
The law of supply and demand is a crucial concept in economics that significantly impacts the apparel industry. By understanding and anticipating changes in supply and demand, fashion brands can make informed decisions about production, pricing, and inventory management. This not only helps in meeting consumer needs but also ensures business sustainability in a competitive market.
Innovation and advanced PLM systems further enhance the ability of fashion brands to manage supply and demand effectively. Technological advancements, sustainable practices, and personalized marketing strategies all contribute to a more responsive and efficient fashion industry. Additionally, maintaining supply chain resilience through risk management, technology integration, and agile supply chains is essential for navigating the complexities of the apparel market.
As consumer preferences evolve and new trends emerge, the interplay of supply and demand will continue to shape the fashion landscape, driving innovation and growth in this dynamic sector. By leveraging demand forecasting, optimizing supply chain performance, and enhancing supply chain resilience, apparel brands can thrive in an ever-changing market environment.




