Introduction
In the fast-moving fashion industry, product data management (PDM) is more than just a tool—it’s the backbone of accuracy, collaboration, and operational efficiency. Every single product detail, whether it exists in early design sketches, digital CAD files, or final production specifications, must remain consistent and accessible to multiple teams across different time zones.
PDM systems often provide additional capabilities beyond basic data storage, such as enhanced collaboration tools or workflow automation.
Inaccuracies don’t just cause inconvenience, they can lead to costly manufacturing mistakes, delayed deliveries, and wasted materials. For fashion companies, PDM systems aren’t optional—they are essential. Wave PLM began its journey as a robust PDM system and has since evolved into a comprehensive PLM platform, combining the strengths of PDM with advanced lifecycle management features designed for today’s apparel market.
Defining PDM
PDM meaning: Product Data Management is a records-based system that centralizes and controls all product-related data and files in a secure digital space. With PDM software, you can organize design files, track version changes, and ensure that every authorized user is working with the latest approved information.
PDM Definitions and Key Principles
- Central Database – A single, secure location where all product files live.
- Version Control – Track every change and prevent outdated files from being used.
- Collaboration Hub – Enable designers, sourcing teams, and manufacturers to work with the same accurate data.
- Metadata Management – Add important details like fabric composition, measurement units, and compliance certifications to product files.
PDM in Fashion
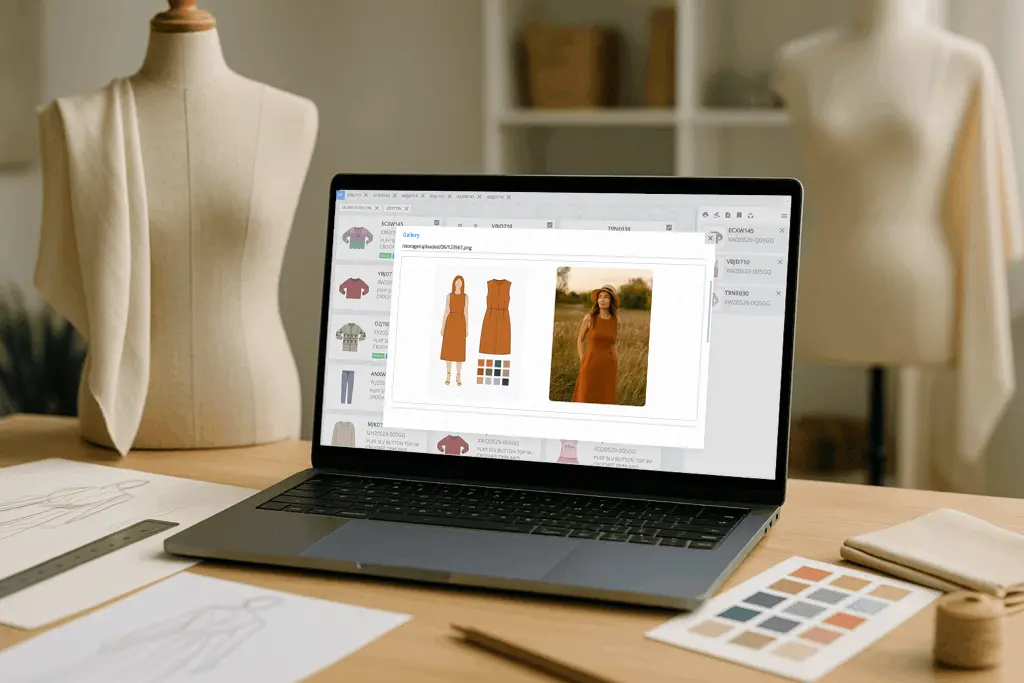
In fashion and apparel, PDM does far more than store CAD drawings. It manages fabric specifications, size charts, line sheets, tech packs, high-resolution product images, and integrates seamlessly with clothing design apps that enhance creativity and design efficiency. Updates to these assets—like a change in fabric weight, stitch type, or trim selection—are instantly visible to everyone who needs them.
These systems also enable users to quickly find and access the files or data they need, improving productivity and reducing the time spent searching for important documents or resources.
Example: Imagine a designer updates the collar shape for a jacket. Without PDM, this update could easily be lost in email threads or forgotten during meetings. With PDM, the change is logged, versioned, and immediately accessible to the production team, reducing miscommunication and saving valuable time.
Core Features of PDM Systems
|
Function |
Description |
Fashion Example |
|---|---|---|
|
CAD File Management |
Store and organize design files. |
Keep Illustrator patterns in a central, searchable system. |
|
Version Control |
Track and control file changes. |
Ensure tech packs used in production are always the latest version. |
|
BOM Management |
Manage product contents and components. |
Record every fabric, trim, button, and label detail. |
|
Approval Process |
Define clear milestones in product development. |
Approve pre-production samples before mass manufacturing. |
|
Data Security |
Restrict access to sensitive files. |
Protect unreleased collections from leaks. |
|
Metadata Control |
Organize detailed product data. |
Include care instructions, weight, and compliance details. |
|
External Integration |
Connect to ERP, PLM, and design tools. |
Link PDM data directly to sourcing and manufacturing workflows. |
PDM systems can be installed using various methods, such as on-premises deployment, cloud-based services, or hybrid approaches. Installation can be tailored to different user sites or isolated environments, depending on company requirements and operating systems. Many solutions also provide downloadable product specifications and technical documents in PDF format, allowing users to easily download and save important information.
Relationship with Other Systems
PDM systems do not operate in isolation—they are designed to seamlessly connect with other essential business and design platforms. By integrating with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, PDM enables companies to manage product data, bills of materials, and manufacturing processes within a unified environment. This integration streamlines the flow of information, reducing manual data entry and ensuring that every unit of product data is consistent across departments.
When connected to Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools, PDM systems allow for real-time management of design files and automatic extraction of metadata. This means that every design update, file change, or new version is instantly captured and made available to the right teams, saving time and minimizing errors. As a foundational layer within Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems, PDM provides the structure needed to manage product data, design iterations, and development processes from concept to manufacturing. For companies looking to build a powerful, central data management ecosystem, PDM is the key to connecting design, development, and business management into one cohesive system.
Why Product Data Integrity Matters
Data integrity means that product information stays accurate, consistent, and reliable from concept to retail. A single error in product data—like an incorrect size spec or missing material code—can result in production delays, rejected shipments, or financial losses. Errors in product data may lead to various issues, such as unexpected production delays or significant financial losses, highlighting the importance of maintaining data integrity. PDM systems prevent these issues by ensuring everyone accesses the same verified information, boosting trust and efficiency across teams.
Revision Control and Management
Effective revision control and management are at the heart of any successful PDM system. In fast-paced product development environments, companies need to manage multiple design files, track changes, and control access to sensitive information—all while ensuring that the latest product data is always available. PDM systems provide robust features such as check-in and check-out functionality, detailed version histories, and automated workflows that help manage complex design projects.
By using these tools, teams can easily check which changes have been made, who made them, and when. This level of control not only reduces the risk of errors but also ensures that every stakeholder is working with the most current information. Whether managing a single product or a range of variants, PDM’s revision control features help companies maintain compliance, streamline collaboration, and keep every file and design update organized and accessible.
PDM Security and Compliance
Protecting sensitive product data is a top priority for companies in today’s competitive and regulated markets. PDM systems are built with advanced security and compliance features to ensure that only authorized users can access, manage, or modify product information and files. With granular user permissions, encryption, and audit trails, PDM provides full control over who can view or edit data, helping companies safeguard their intellectual property and confidential designs.
Compliance is equally important, especially for industries that must adhere to strict standards such as ISO 9001 or FDA regulations. PDM systems support these requirements by tracking changes, maintaining detailed records, and ensuring that all product data meets industry and regulatory standards. By using PDM, companies can confidently manage their product information, knowing that their data is secure, compliant, and always under control.
Wave PLM: From PDM Roots to PLM Power
Wave PLM started as a dedicated PDM system tailored for fashion companies. Its early purpose was to store and manage design files, control technical changes, and ensure compliance with quality and brand standards. Over time, Wave evolved into a full PLM platform, offering:
- Centralized file and data control.
- Integrated project tracking from design to store launch.
- Manufacturing management for suppliers and factories.
- Sustainability and compliance tracking.
- External integrations with ERP systems, e-commerce sites, and creative applications.
Wave PLM also integrates with cloud-based services to streamline product lifecycle management.
Today, Wave PLM blends the precision of PDM with the full visibility of PLM, giving brands the power to manage an entire product lifecycle in one place.

PDM vs. PLM in Fashion
|
Feature |
PDM |
PLM |
|
Focus |
Data and file management |
Full product lifecycle management |
|
Scope |
Design and technical data |
Concept, design, sourcing, production, logistics |
|
Best For |
Teams that need strict data control |
Companies managing all operations from idea to delivery |
|
Integration |
CAD and documentation systems |
Integrated sourcing, manufacturing, and sales processes |
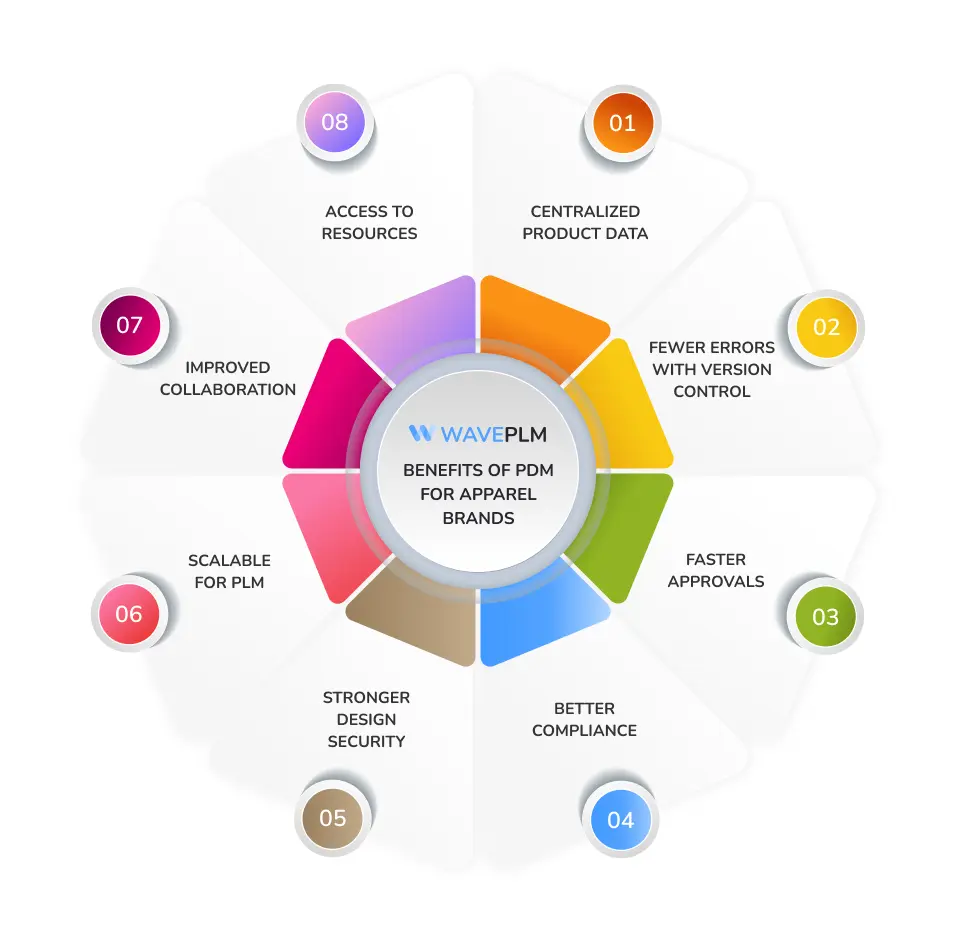
Benefits of PDM for Apparel Brands
- Centralized storage for all product files and metadata.
- Reduced errors through version control and change tracking.
- Faster approvals thanks to real-time access to accurate data.
- Improved compliance with safety and sustainability standards.
- Enhanced protection for sensitive and unreleased designs.
- A scalable foundation for upgrading to PLM.
- Better collaboration between in-house teams and external partners.
- Access to educational resources to learn best practices and improve workflow efficiency.
Implementing PDM in Your Brand
- Set Clear Goals – Identify the problems PDM will solve.
- Choose the Right PDM Package – Ensure the software supports fashion workflows. Evaluate different methods for implementing PDM, such as cloud-based or on-premises solutions, to determine the best fit for your organization.
- Train All Users – Equip staff to manage files and data confidently.
- Integrate with External Applications – Link to ERP, PLM, and design tools.
- Maintain Data Quality – Regularly review and update product contents.
- Set Approval Workflows – Establish checkpoints for change control.
- Plan Installation Site – Decide whether to install PDM at a specific user site or across multiple locations, depending on your organizational needs.
PDM Best Practices
To unlock the full value of a PDM system, companies should adopt proven best practices for data and product management. Start by defining a clear data management strategy that aligns with your business goals and product development needs. Standardize workflows to ensure consistency in how files and information are managed, and provide comprehensive training so users can confidently use the system’s features.
Integrating PDM with other business systems, such as ERP and CAD, is essential for creating a central source of truth for all product data. Regularly back up your data, conduct security audits, and keep your software updated to protect against data loss and security threats. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of your PDM system will help you adapt to changing business requirements and ensure that the system continues to provide value. By following these best practices, companies can improve collaboration, reduce errors, and empower users to manage product data efficiently and securely.
Quick PDM Checklist
|
Task |
Status |
|
Centralize all product files |
☐ |
|
Apply version control |
☐ |
|
Create approval workflows |
☐ |
|
Integrate with CAD tools |
☐ |
|
Train users on data management |
☐ |
|
Audit metadata regularly |
☐ |
Conclusion
PDM isn’t just a filing cabinet for digital assets—it’s the control center for product development in the fashion industry. By understanding what is PDM and leveraging it for accurate data management, brands can improve speed to market, reduce costly mistakes, and strengthen collaboration.
PDM empowers brands to make products with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Wave PLM builds on its PDM foundation, offering a future-ready solution that merges precision data control with full lifecycle management for fashion brands aiming for growth without compromise.




