
Circular fashion reshapes the fashion industry with a system that keeps materials in use. The concept of circular fashion serves as a foundational idea guiding sustainable practices and the shift from linear to circular models. The circular model replaces the traditional linear model. The linear model drives textile waste, water pollution, and has a high impact on the environment. Circular fashion initiatives aim to minimize waste, focus on reducing waste, reduce waste generation, and support a closed loop system. The term circular fashion describes a shift in the textile industry toward innovative business models, eco friendly materials, and sustainable materials. Fashion brands use digital tools to create longer lifespans for garments. They design fashion products made for repair, recycling, and reuse.
This guide explains how technology supports the circular economy. It also shows how PLM tools help teams build circular systems within the fashion industry. You will see key principles, examples, and a checklist for implementing circular fashion.
Why Traditional Tools Fail Circular Fashion — Challenges With Linear Systems
The traditional linear model moves from raw materials to production, then to disposal. Many fashion brands follow this system. Fast fashion accelerates this cycle. It increases textile waste, waste generation, and environmental impact. This linear approach also contributes significantly to climate change, as unsustainable production and disposal methods release greenhouse gases and deplete natural resources.
Linear tools fail because teams cannot track materials across the full life cycle. They lose data and cannot measure the impact of new clothes or new garments. Waste is produced during manufacturing processes and often stays invisible. Recycling programs work with weak data. Repair services cannot predict common defects. Fashion companies struggle to create a closed loop system.
Key issues appear fast:
- Designers cannot track materials across the life cycle.
- Teams cannot see how fashion products become waste.
- Suppliers cannot share information about eco friendly materials.
- Circular systems break when data stays hidden.
The fashion industry needs tools that support circular practices at scale.
Key Requirements for Circular Supply Chains: Traceability, Material Data, Lifecycle Tracking
Circular fashion depends on rich, clear data. Fashion brands need systems that support traceability, transparency, and circular economy principles.
Traceability
Teams track raw materials, garments, trims, treatments, and finishes. They see where textiles come from and how suppliers produce them. They monitor environmental impact across each step.
Material Data
Designers need accurate data about sustainable materials, eco friendly materials, and new materials. They need to see blends, chemical finishes, and durability scores. This helps them create clothing with longer lifespans.
Lifecycle Tracking
Garments move through many loops. Clothing may pass through repair, secondhand clothing markets, thrift shops, resale, or recycling programs. Online platforms extend the life of fashion. Teams monitor how textiles get recycled and how they re-enter production.
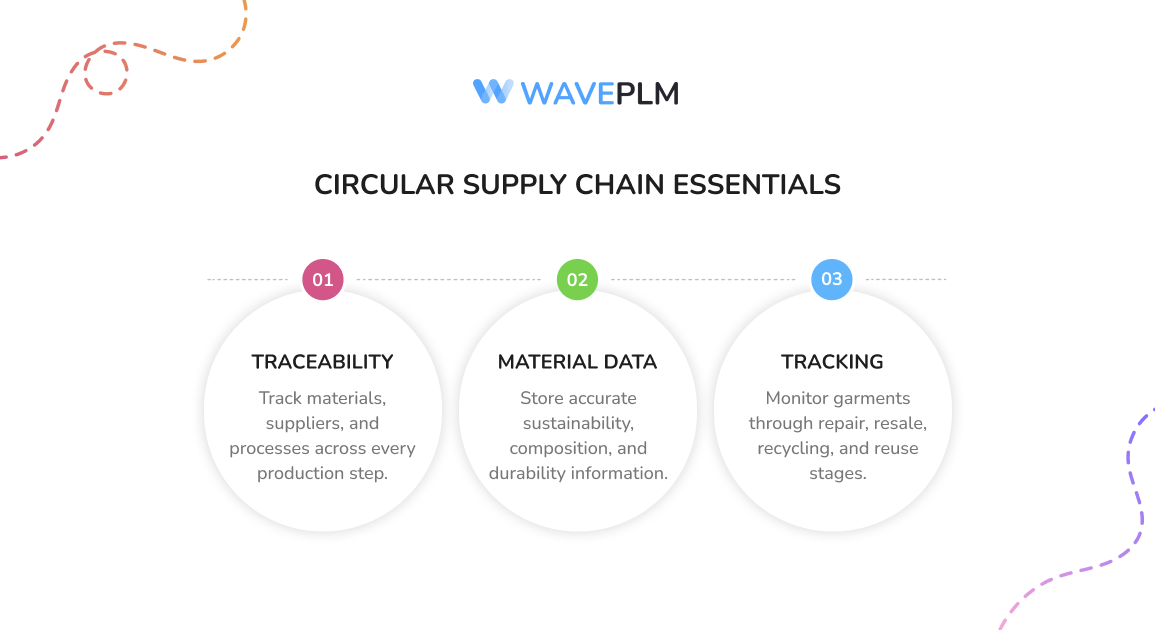
Table: Core Data Needs for a Circular Fashion Model
|
Requirement |
What Teams Track |
Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
|
Traceability |
origins, batches, certifications |
supports recycling and reduces waste |
|
Material Data |
blends, finishes, durability |
improves design and minimizes waste |
|
Lifecycle Tracking |
repair data, resale, recycling |
builds strong circular systems |
These features help brands create fashion systems built for the future.
How PLM Software Supports Circular Fashion — centralizing materials, versions, waste tracking, reuse, recycling data
PLM tools support implementing circular fashion. They create one location for all materials, fashion products, and lifecycle information.
Here is how PLM strengthens a circular fashion model:
Centralized Material Libraries
Teams store textiles, trims, blends, and certifications. They manage eco friendly materials, recycled textiles, and raw materials.
Version Control
Designers update patterns and materials. PLM stores each version. Teams track how changes affect recycling and waste.
Waste Tracking
PLM records production waste. Teams track offcuts, leftover rolls, and scrap. They find ways to minimize waste.
Reuse and Recycling Data
PLM stores data about repair, reuse, and recycling. It supports a closed loop system where textiles get continuously cycled.
PLM connects people and data. It helps fashion brands shift from fast fashion habits to sustainable fashion systems.

Digital Tools & Innovations That Help
Research from MDPI and insights from the Ellen MacArthur foundation show how digital tools strengthen the circular economy. These tools help address waste and environmental impact by enabling better tracking, recycling, and sustainable production processes. As more people adopt digital tools and circular fashion practices, the industry is seeing a shift toward greater sustainability and reduced environmental harm.
Textile-Traceability Databases
These databases track materials, finishes, and supplier data. They help recyclers reduce contamination.
Digital Recycling Platforms
Recyclers and brands share information about inputs and outputs. This improves recycling rates and reduces waste.
AI and Data Tracking
AI analyzes clothing returns, repair needs, and textile waste. Teams redesign garments to reduce the environmental impact.
Material Passports
Passports store detailed data about garments, materials, and repair notes. They support reuse and recycling.
Template: Material Passport Structure
|
Field |
Description |
|
Material Composition |
blends, treatments |
|
Source |
supplier and certification |
|
Expected Lifetime |
durability score |
|
Repair Notes |
guidance and parts needed |
|
End-of-Life Path |
recycling or reuse |
These digital tools help brands scale circular fashion.
Case Examples: Brands or Suppliers Who Use Tech + PLM for Circular Workflows
MDPI and the Ellen MacArthur foundation highlight how brands use technology to support circular systems.
Consumers also play a key role in supporting and participating in circular fashion initiatives by choosing to repair, reuse, and buy secondhand clothing, as well as advocating for more sustainable industry practices.
Example 1: A brand that tracks recycled fibers with PLM
A global outdoor brand built a digital material library. They tracked recycled fibers and reduced textile waste. This improved recycling quality.
Example 2: A supplier that uses digital IDs for yarn batches
A supplier created IDs for yarn. These IDs tracked chemical treatments and durability. Designers removed materials that harmed recycling.
Example 3: A fashion company that uses AI repair insights
One apparel brand used AI to study repair needs. They reinforced weak areas on garments. This reduced waste and improved product life.
These examples show how fashion brands improve sustainability at scale.
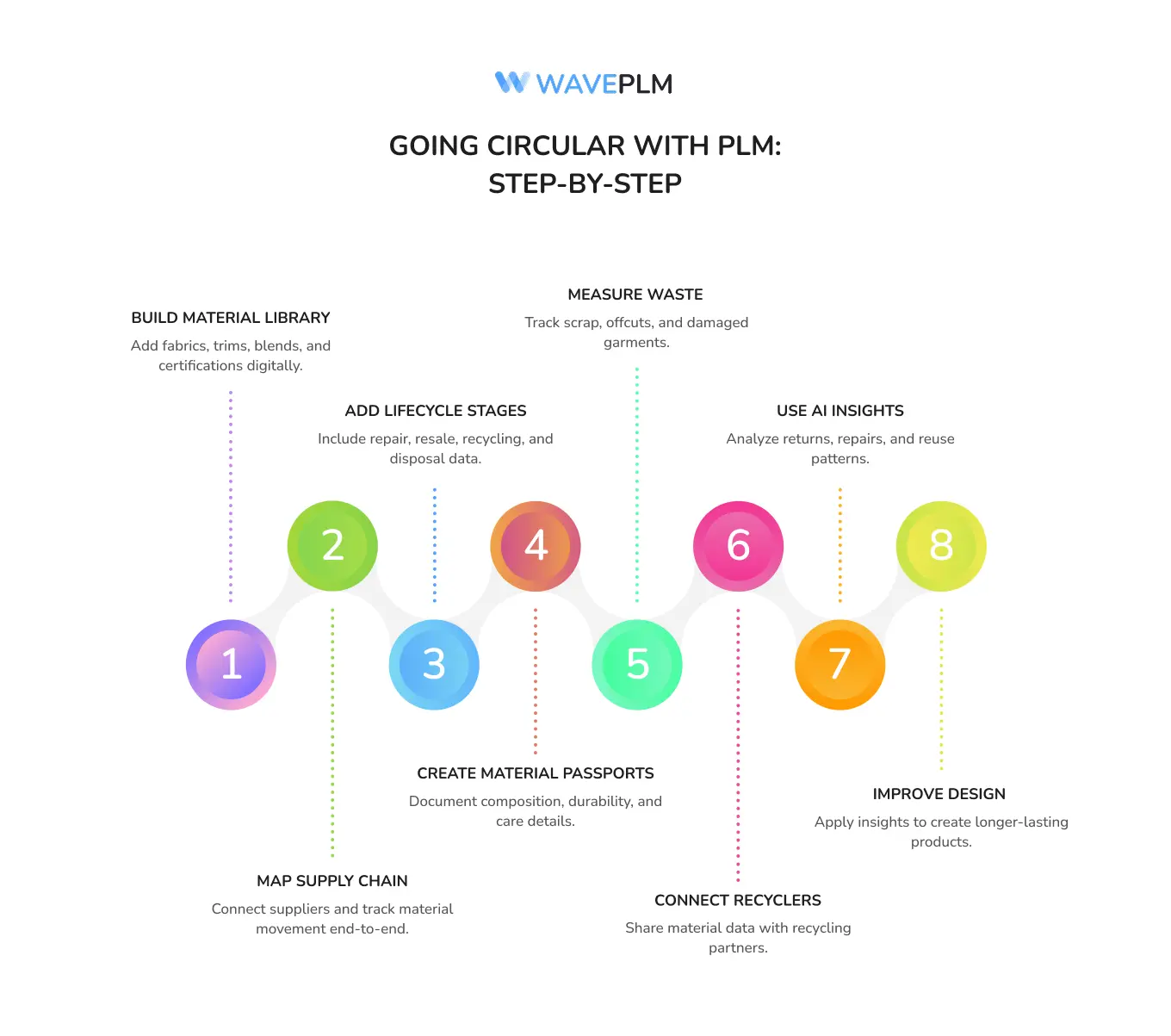
Step-by-Step Checklist for a Brand to Go Circular Using Tech + PLM
This checklist helps teams implement circular fashion.
Step 1: Build a Digital Material Library
Add textiles, trims, blends, and certifications.
Step 2: Map Supply Chain Data
Track suppliers and material flows.
Step 3: Add Lifecycle Stages to PLM
Include repair, resale, recycling, and disposal data.
Step 4: Create Material Passports
Add composition, durability, and repair notes.
Step 5: Measure Waste
Track scrap, offcuts, and damaged garments.
Step 6: Connect Recycling Partners
Share material data with recycling teams.
Step 7: Use AI Insights
Analyze returns and repair patterns.
Step 8: Improve Designs
Use data to create new clothing with lower environmental impact.
Checklist Table
|
Step |
Action |
Output |
|
1 |
Build library |
data foundation |
|
2 |
Map supply chain |
traceable flows |
|
3 |
Add lifecycle stages |
full history |
|
4 |
Create passports |
circular-ready products |
|
5 |
Measure waste |
hotspot analysis |
|
6 |
Connect recyclers |
cleaner loops |
|
7 |
Use AI |
improved decisions |
|
8 |
Improve designs |
stronger circular model |
How Wave PLM Helps: Features & Workflow
Wave PLM supports circular fashion across the system.
Material Libraries
Teams store textiles, blends, trims, and certifications.
Supplier and Traceability Tools
Teams track materials across tiers.
Lifecycle Views
Teams see each stage of the life cycle.
Fast Collaboration Tools
Suppliers share updates in real time.
Wave PLM helps brands create sustainable fashion systems and reduce environmental impact.

Conclusion & Next Steps
Circular fashion supports the circular economy and reduces textile waste. It helps the planet and allows economic growth. The fashion industry must use technology to build stronger systems. PLM tools give brands the data they need to create sustainable materials, reduce waste, and design new garments for the future.
Wave PLM offers the tools to build these circular systems. Fashion companies can start now. Map materials, track garments, and create your first circular workflow. Prepare for your next event and show real progress in sustainability.
Use technology to create clothes that stay in the loop and support a cleaner planet.





Leave a Reply