
In the fast-paced world of fashion, staying ahead often means embracing innovation. As technology continues to reshape various industries, the fashion sector is no exception. The industry constantly seeks new ways to streamline processes, reduce costs, and foster creativity. One of the most promising advancements in recent years is the concept of virtual sampling and prototyping. This approach has the potential to revolutionize how garments are designed, tested, and brought to market.
Virtual sampling and prototyping are fundamentally changing the landscape of fashion design by utilizing digital tools and technologies. These methods allow fashion brands to create and visualize garments in a virtual environment, significantly speeding up the design process and reducing reliance on physical samples.
At the core of this transformation is Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software. PLM software serves as a comprehensive platform for managing the entire lifecycle of a product, from initial concept through to production and beyond. This article will explore how these advancements are shaping the future of the fashion industry and the myriad benefits they bring to designers, manufacturers, and consumers alike, making a brand-new virtual fashion.
Understanding Virtual Sampling and Prototyping
Traditionally, the fashion industry heavily relies on physical prototypes and samples to bring designs to life. However, this approach is time-consuming, resource-intensive, and often leads to multiple iterations before finalizing a product. Enter virtual sampling and prototyping, a digital solution that allows designers to create, visualize, and modify garments in a virtual environment before anything is physically produced.
We at the Wave PLM team bring a wealth of experience to the table. With over 20 years in the industry, we have helped our customers send, track, and make decisions on millions of samples of various products. This extensive experience gives us deep insights into the challenges and opportunities in the field of virtual sampling and prototyping. And we know where the wind blows in this industry.
Virtual sampling involves using 3D modelling and simulation techniques to create digital versions of physical garments. With advanced software, designers can simulate the appearance, texture, and fit of clothes on a computer screen. This technology allows designers to experiment with different fabrics, textures, and styles in real time, making changes quickly without waiting for physical prototypes. As a result, the design process becomes faster and more cost-effective, reducing the need for multiple physical samples. This not only saves time and money but also fosters greater creativity and experimentation, as designers can easily try out new ideas and perfect their designs digitally before any fabric is cut.
Primary types of virtual sampling:
1. 2D Digital Sampling
- Sketching and Flat Patterns: Designers use 2D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create digital sketches and flat patterns of garments. This method involves drawing the garment outlines and details on a flat surface, which can then be used to plan the construction of the garment.
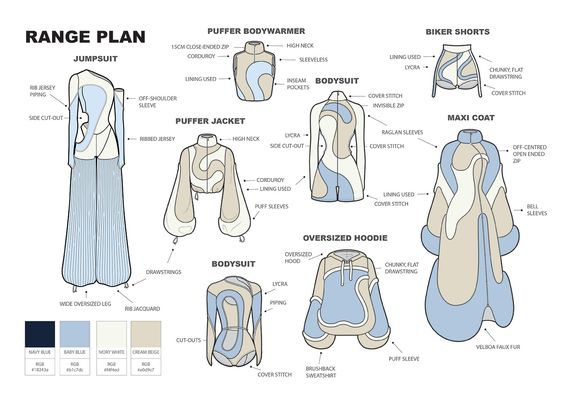
- Textile Design: 2D sampling is also used for designing textile prints and patterns. Designers can create and modify intricate patterns, colorways, and layouts digitally, which can be applied to virtual garment samples.
2. 3D Digital Sampling
- 3D Garment Modeling: This involves creating a three-dimensional model of the garment using specialized 3D fashion design software. Designers can manipulate the model to visualize how the garment will look from all angles.
- Virtual Fitting: 3D sampling allows for virtual fitting sessions where the digital garment can be placed on a 3D avatar. Designers can adjust the fit, see how the fabric drapes on the body, and make real-time modifications.
- Fabric Simulation: Advanced 3D software can simulate different fabric properties, such as texture, weight, and stretch. This helps designers understand how the garment will behave with various materials.

3. Virtual Reality (VR) Sampling
- Immersive Design Review: VR technology enables designers and stakeholders to immerse themselves in a virtual environment where they can interact with the garment. This provides a more intuitive and realistic evaluation experience.
- Collaborative Virtual Spaces: Teams can collaborate in a shared virtual space, discussing and modifying designs in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This fosters better communication and quicker decision-making.
4. Augmented Reality (AR) Sampling
- Augmented Prototyping: AR allows designers to overlay digital garments onto physical mannequins or models. This hybrid approach helps in visualizing how a digital design integrates with the real world.

- Consumer Engagement: AR can be used to provide consumers with virtual try-on experiences, where they can see how garments look on their bodies through their smartphones or AR devices. This enhances the shopping experience and can reduce return rates.
5. Digital Material Libraries
- Material Scanning: Digital material libraries store high-resolution scans of various fabrics, including their textures, colors, and physical properties. Designers can choose from these digital swatches to use in their virtual samples.
- Customization: These libraries can be customized to include specific materials used by a brand, ensuring consistency and accuracy in virtual sampling.
6. Photorealistic Rendering
- High-Quality Visuals: Photorealistic rendering techniques produce highly detailed and lifelike images of digital garments. This is useful for marketing purposes, as it allows brands to showcase their designs in a realistic manner before physical production.
- Lighting and Environment Simulation: This type of virtual sampling can simulate different lighting conditions and environments, helping designers see how the garment will appear in various settings.
The Role of PLM Software in Virtual Sampling
At the heart of virtual sampling and prototyping lies Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software. PLM software provides a centralized platform for managing product customer data, from initial concept to final production. While PLM has long been used in industries like manufacturing and automotive, its application in fashion is relatively recent but increasingly essential.
PLM software streamlines the entire product development process, facilitating collaboration between designers, manufacturers, and other stakeholders. It serves as a digital hub where all product-related information, including designs, materials, and specifications, are stored and accessible in real time. By integrating virtual sampling capabilities into PLM platforms, fashion companies can achieve greater efficiency, agility, and innovation in their design processes.
Benefits of Virtual Prototyping with PLM
The adoption of virtual prototyping with Product Lifecycle Management software offers numerous benefits across the fashion industry, transforming how designers and manufacturers approach garment creation. Here are some of the key advantages:
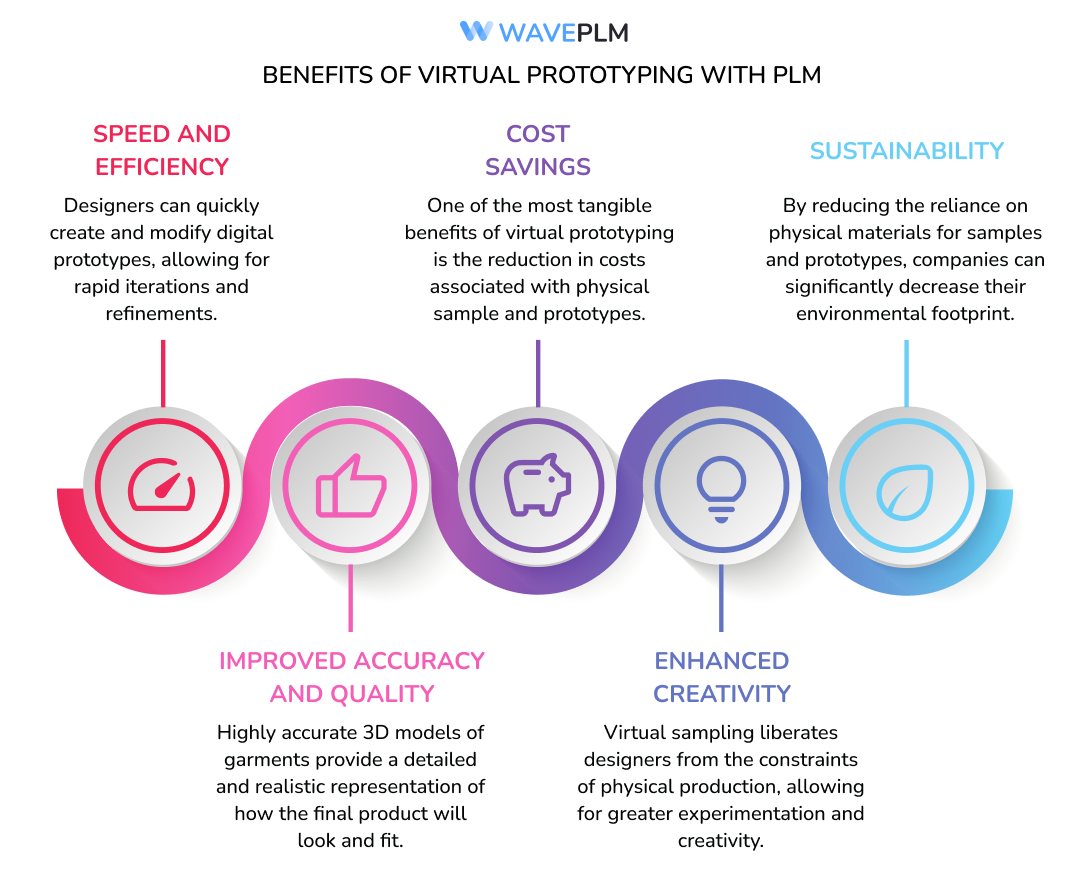
1. Speed and Efficiency:
Virtual sampling significantly accelerates the design process. Designers can quickly create and modify digital prototypes, allowing for rapid iterations and refinements. This speed translates to faster time-to-market, enabling fashion companies to respond swiftly to trends and consumer demands. PLM software enhances this efficiency by enabling seamless collaboration among design teams, manufacturers, and other stakeholders, thus reducing delays and miscommunications that often occur in traditional workflows.
2. Cost Savings:
One of the most tangible benefits of virtual prototyping is the reduction in costs associated with physical sample and prototypes. Traditional methods require multiple iterations of samples, each involving material costs, labour, and shipping expenses. Virtual sampling minimizes these needs, leading to significant savings in materials and production costs. Additionally, companies can avoid the substantial shipping and logistics expenses associated with transporting samples between design teams, manufacturers, and clients.
3. Improved Accuracy and Quality:
It allows designers to create highly accurate 3D models of garments. These digital models provide a detailed and realistic representation of how the final product will look and fit. By visualizing the garment in 3D, designers can identify and correct potential issues early in the design process, reducing the likelihood of errors during production. This precision leads to higher quality products, as the final garments are more likely to meet the desired specifications and standards.
4. Sustainability:
The fashion industry is under increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Virtual prototyping offers a greener alternative to traditional manufacturing methods. By reducing the reliance on physical materials for samples and prototypes, companies can significantly decrease their environmental footprint. Less material waste and fewer physical samples mean lower consumption of resources and reduced carbon emissions. This shift towards digital processes supports the industry’s move towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly supply chain.
5. Enhanced Creativity:
Virtual sampling liberates designers from the constraints of physical production, allowing for greater experimentation and creativity. Designers can easily test and visualize different designs, fabrics, and patterns in a digital environment. This flexibility fosters innovation, enabling the creation of more unique and compelling products. The ability to experiment without the time and cost penalties associated with physical samples encourages designers to push the boundaries of their creativity and explore new ideas that might not have been feasible otherwise.
Challenges and Considerations
While the adoption of virtual sampling with PLM offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the initial investment required to implement PLM software. This includes not only the cost of the software itself but also the expense associated with training staff to effectively use these new tools. For many companies, especially smaller ones, this can represent a significant financial commitment.
Furthermore, ensuring the accuracy and realism of virtual prototypes can be a complex task. Accurately representing the intricate textures, behaviors, and drapes of various fabrics in a virtual environment remains a technical challenge. Fabrics behave differently under various conditions, and replicating this in a digital model requires sophisticated algorithms and high-quality data. The visual and functional fidelity of these virtual prototypes must be high enough to provide reliable insights during the design process.
Additionally, while virtual prototyping can streamline the design process considerably, it cannot entirely replace the need for physical samples. Physical samples are essential for assessing the true quality and fit of garments on real bodies. The tactile feedback and real-world testing of materials, seams, and overall garment construction are aspects that virtual sampling cannot fully replicate. Thus, companies must strike a balance between virtual and physical prototyping to ensure the best possible outcomes. This hybrid approach ensures that while the efficiency and cost benefits of virtual prototyping are leveraged, the irreplaceable insights gained from physical samples are not lost.

Conclusion
The future of virtual sampling and prototyping with PLM software is indeed promising. This technology offers fashion companies a powerful tool to drive innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. By embracing digital garment creation and 3D fashion design, businesses can stay ahead of the curve in an increasingly competitive market. The integration of virtual prototyping into the fashion design process enables faster and more cost-effective development cycles, reduces waste, and fosters greater creative exploration.
As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for virtual sampling will expand, further reshaping the way we design and produce clothing. The ongoing advancements in 3D modelling, artificial intelligence, and materials science will enhance the realism and functionality of virtual prototypes, making them even more indispensable in the design process.
In this dynamic landscape, companies that invest in and adapt to these digital tools will be well-positioned to lead the industry. They will benefit from the immediate advantages of speed and cost savings and long-term gains in sustainability and innovation. The future of fashion is digital, and virtual sampling with PLM software is at the forefront of this transformation, paving the way for a more efficient, creative, and eco-friendly industry.





Leave a Reply