
The global garment industry plays a crucial role in the modern economy, providing clothing for billions of people worldwide. Within this industry, the operations of a modern garment factory are a complex and dynamic process that involves various stages from design to distribution.
Garment factory serves as the backbone of the fashion industry, tirelessly producing the clothes that fill our closets and adorn our bodies.
Behind every garment lies a complex process involving skilled labor, intricate machinery, manufacturing and meticulous attention to detail. This article will delve into the inner workings of a large contemporary garment factory, exploring each stage of production and shedding light on the technologies, sustainability efforts, and challenges faced by the industry.
1. Design and Fabric Selection
The journey of a garment begins with the creative process of design. Talented designers work on creating sketches and digital renderings, considering trends, functionality, and market demands. Once a design is finalized, the next step is prototyping. Modern garment factories utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software and 3D printing to create prototypes, allowing for faster iterations and efficient adjustments before mass production.
Fabric selection is a crucial initial step in garment production. Textile experts carefully choose fabrics based on factors like quality, durability, and design suitability. Considerations such as fabric weight, texture, and color are taken into account to meet the specifications of the clothing line. Sustainable and ethically sourced materials are increasingly prioritized by garment manufacturers.
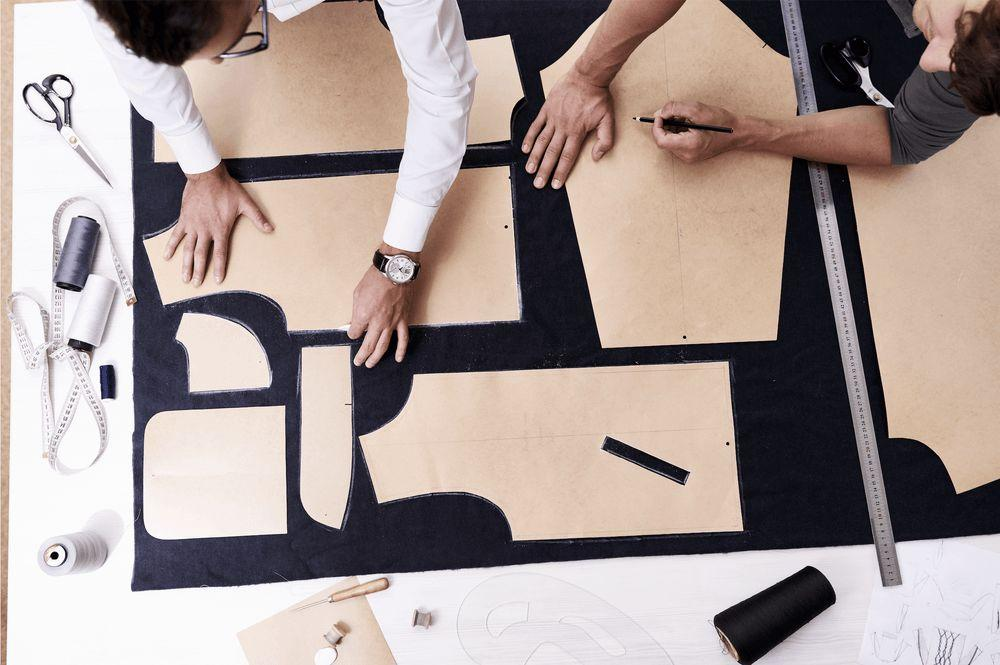
2. Pattern Making and Cutting
Once the fabric is selected, the pattern-making process begins. Skilled pattern makers draft templates based on design specifications and garment sizes. These patterns serve as guides for cutting the fabric. Fabric is laid out in layers, and the patterns are carefully positioned to minimize waste.
Raw materials are an essential part of any garment, and sourcing them responsibly is really important for a sustainable supply chain. Factories partner with textile suppliers, often adopting eco-friendly materials and considering ethical sourcing practices.
Once materials are acquired, automated cutting machines, guided by computer algorithms, ensure precise cuts, minimizing waste and optimizing material utilization.

3. Sewing and Assembly
Sewing is where the magic happens, as individual fabric pieces are transformed into garments. Skilled workers handle intricate tasks such as attaching collars, sleeves, and decorative elements. They operate sewing machines and other equipment to piece together the fabric, following patterns and guidelines.
The assembly line is the heart of garment production. Automation has significantly improved efficiency in this stage, with robotic arms and automated stitching reducing the time and labor required. However, a balance must be struck to support and preserve the craftsmanship and artistry of garment creation.
4. Quality Control in Garment Industry
Rigorous quality control measures are implemented at various stages of production to ensure that each garment meets the required standards. Manual and automated inspections are conducted to identify defects, irregularities, and deviations from the specifications. Modern factories invest in technology like computer vision and artificial intelligence to enhance and improve the accuracy and speed of control processes.
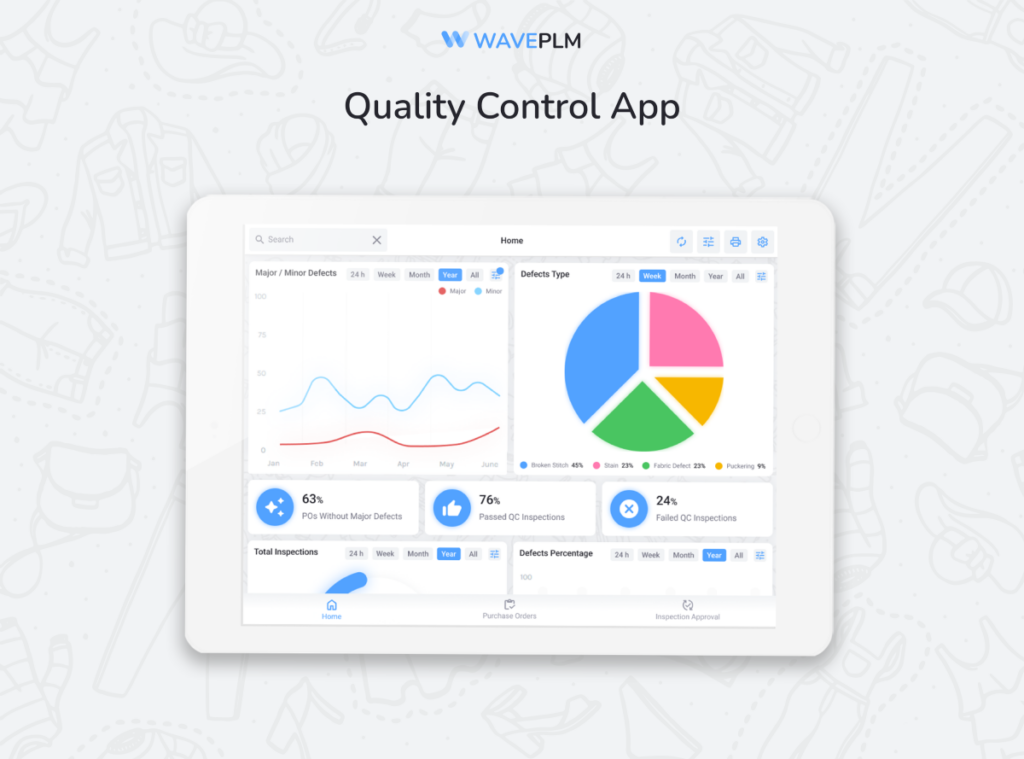
Wave PLM has their own decisions and complex approach to quality control for final products, with the web version of Quality Control and an App for mobile devices, which provide convenience for quality inspectors in the field: in factories and warehouses.
5. Finishing and Packaging
Once the garments pass quality control, they undergo finishing processes such things such as ironing, steaming, and adding labels. Packaging is another critical aspect, with a focus on sustainable materials and eco-friendly practices. Factories often implement innovative packaging designs that minimize waste and contribute to the overall sustainability goals of the industry.

6. Distribution and Logistics
The distribution phase involves transporting finished garments to retailers or directly to consumers. Advanced logistics systems, powered by data analytics and automation, manage inventory, track shipments, and optimize delivery routes. E-commerce has transformed distribution channels, with many factories now focusing on direct-to-consumer models, reducing reliance on traditional retail networks.
7. Technology Integration and Sustainability
Modern garment factories are embracing technology to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Robotics, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are integral to operations, enabling faster production cycles and better resource management. Sustainability is a growing concern, prompting factories to adopt eco-friendly practices, recycle materials, and implement ethical labor standards.
The garment industry’s environmental footprint is significant, with issues such as water pollution, waste generation, and carbon emissions. Sustainable practices, such as using organic or recycled materials and implementing eco-friendly production processes, are gaining traction. Efforts to reduce water and energy consumption, minimize waste, and other ways to implement circular economy principles are being pursued. Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and accountability from brands regarding their environmental practices.

8. Challenges and Future Trends
Despite technological advancements, the garment industry faces challenges such as fluctuating demand, geopolitical issues affecting the supply chain, and the need for continuous innovation. The future holds promising trends, including the rise of circular fashion, increased use of recycled materials, and a focus on transparency and traceability throughout production.
Adapting to these challenges and embracing trends requires industry players to prioritize sustainability, innovation, and responsiveness to evolving consumer demands. By doing so, they can position themselves for success in an ever-changing market landscape.
Conclusion
To sum up, a garment factory stands at the intersection of creativity, craftsmanship, and commerce, playing a vital role in the global fashion ecosystem. From the selection of fabrics to the final touches on finished garments, each step in the production process requires skill, experience, precision, and attention to detail.
As the industry evolves, embracing technological advancements, ethical labor practices, and sustainable initiatives will be essential for shaping a more responsible and resilient future for garment manufacturing.
Through collective efforts and innovation, we can ensure that the clothes we wear not only look good but also embody principles of quality, ethics, and sustainability.
Overall, the operations of a modern garment factory are a fascinating blend of creativity, technology, and sustainability. Finding the right balance between efficiency, ethical practices, and environmental responsibility will be crucial. By understanding the intricate processes within these hubs, we can learn to appreciate the complexities involved in bringing fashion from the drawing board to our closets.





Leave a Reply