
SKU rationalization in the fashion business
The fashion industry is characterized by its rapid pace, evolving trends, and diverse consumer preferences. With these dynamics, maintaining an efficient and profitable operation becomes a challenge. Inventory optimization is crucial for improving operational efficiency and reducing costs in the fashion business. Rationalization, particularly SKU rationalization, plays a pivotal role in optimizing the fashion business. Effective SKU rationalization enhances internal tracking, enabling better organization and forecasting of inventory across various retail locations. This article delves into the rationalization meaning and definition, its application in the fashion industry, and how Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems can aid in this process.
Understanding Rationalization in Fashion Business
Rationalization in the context of business refers to the process of making a company or industry more efficient by systematically organising and streamlining processes. In fashion, rationalization acts as a defence mechanism against inefficiencies and threats to business performance, involving the evaluation of various aspects of the business, from production to sales, and implementing changes that reduce waste, lower costs, and improve profitability. Many retailers adopt SKU rationalization to manage their inventory effectively, reduce phantom inventory, and enhance their ability to predict restocking needs.
Rationalization Definition and Meaning
Rationalization means the reorganization of a business’s structure and operations to increase efficiency and effectiveness. Rationalization helps resolve cognitive dissonance in business operations by providing logical justifications for changes. This can include downsizing, merging departments, eliminating redundant processes, or focusing on core competencies. The goal is to create a leaner, more competitive organization that can respond quickly to market changes.
When creating SKU codes, it is important to avoid special characters, as they can lead to confusion in retail software and reduce the clarity of SKUs.
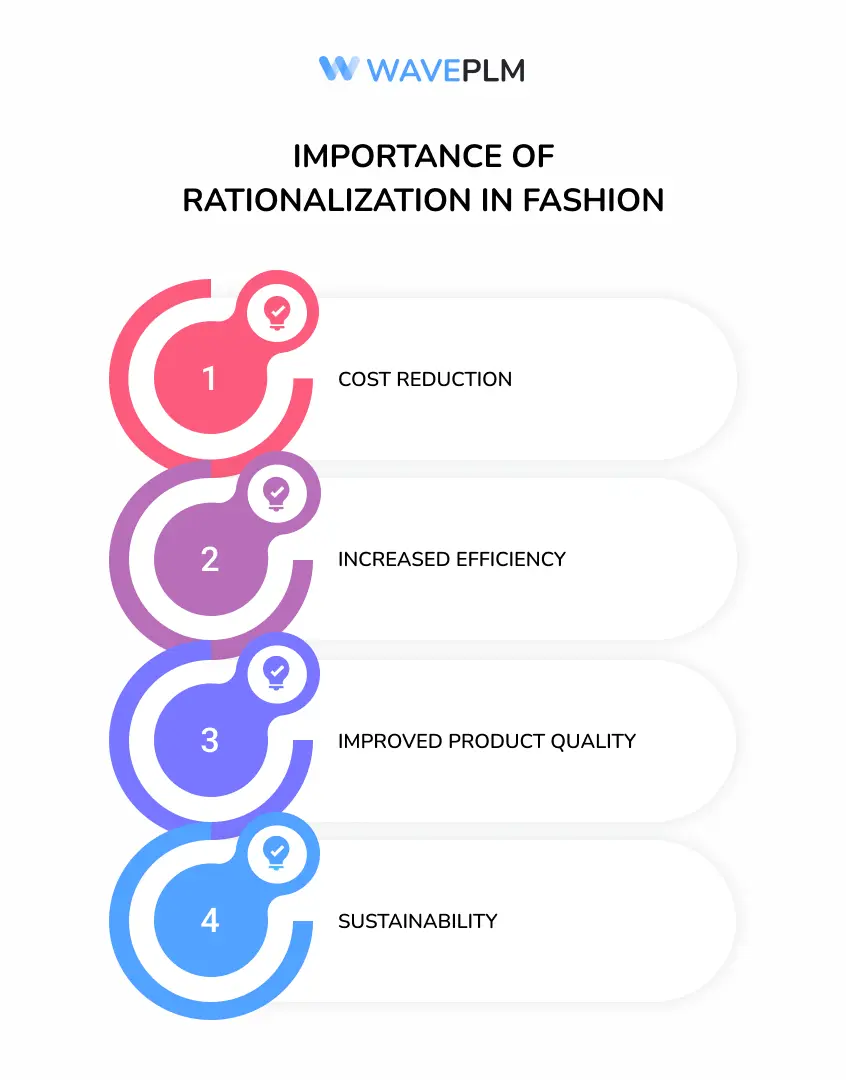
Importance of Rationalization in Fashion
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating unnecessary processes and focusing on high-margin products, fashion companies can significantly reduce their operational costs.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlining operations leads to faster production cycles and quicker response to market trends.
- Improved Product Quality: A more focused production process often results in better quality products, enhancing brand reputation. Maintaining a consistent SKU code for each product variant, such as variations in color and size, is crucial for streamlining inventory management.
- Sustainability: Rationalization can lead to more sustainable practices by reducing waste and optimizing resource use.
Introduction to Stock Keeping Unit
A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a unique identifier for products that enables retailers and businesses to keep track of their inventory more efficiently. SKUs are used to locate and order products, as well as track what items are selling and what items need to be restocked. Using SKUs can help prevent theft and loss of inventory. SKUs are used in inventory management and supply chain processes. Businesses use SKUs to enhance their inventory management and supply chain process. SKUs are a critical component of inventory management and supply chain optimization. (Keep keywords: stock keeping unit, inventory management, stock keeping unit sku, supply chain, unique identifier, sku, skus, keep track, use skus, businesses, inventory)
Creating SKU Numbers
To create a SKU number, start by identifying the most important characteristics of your product, such as season, size, material, color, and more. Use a simple 2-3 letter abbreviation or number to represent each item in your collection. For example, “FW23” for a Fall/Winter 2023 collection. Then, add a simple 2-3 letter abbreviation or number that represents each item in your collection, such as “DRS” for dresses or “JKT” for jackets. Include other distinct details such as size, material, and color information within your SKUs. Finally, include a sequence number to distinguish between individual products within the same subcategory. (Keep keywords: sku number, create a sku, sku, skus, important characteristics)
SKU Number Structure
A SKU number structure typically consists of several codes combined together. It’s a good practice to separate each section into hyphens. For example, “FW23-DRS-S-R-101” for a small red dress. The first section of the SKU number identifies the broadest way to identify the item, such as the season and year. The subsequent sections of the SKU number identify more specifics about the product, such as the product category, size, material, and color. The last part of the SKU number is a sequential number that distinguishes between individual products within the same subcategory. (Keep keywords: sku number, product category, sku, codes, identify)
SKU Rationalization: A Key Component
SKU Rationalization Definition and Meaning
SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) rationalization refers to the process of reviewing and optimizing the number of SKUs a company offers. SKU strategy involves deliberate decision-making related to product assortment and inventory management. This involves analyzing the performance of each SKU and determining which ones are profitable and align with the company’s strategic goals. The aim is to eliminate underperforming or redundant SKUs to streamline inventory, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency.

SKU rationalization – lightspeedhq.com
The Need for SKU Rationalization in Fashion
In the fashion industry, the variety of styles, sizes, and colors can result in an extensive number of SKUs. While variety is essential for meeting diverse consumer preferences, an overabundance of SKUs can lead to several issues:
- Increased Complexity: Managing a vast inventory can be cumbersome and prone to errors.
- Higher Costs: Excessive SKUs increase warehousing costs and complicate the supply chain. SKU optimization can help reduce inventory costs by eliminating low-demand items and minimizing the need for excess stock, thereby improving operational efficiency.
- Reduced Focus: Spreading resources thin across many SKUs can detract from core, high-performing products.
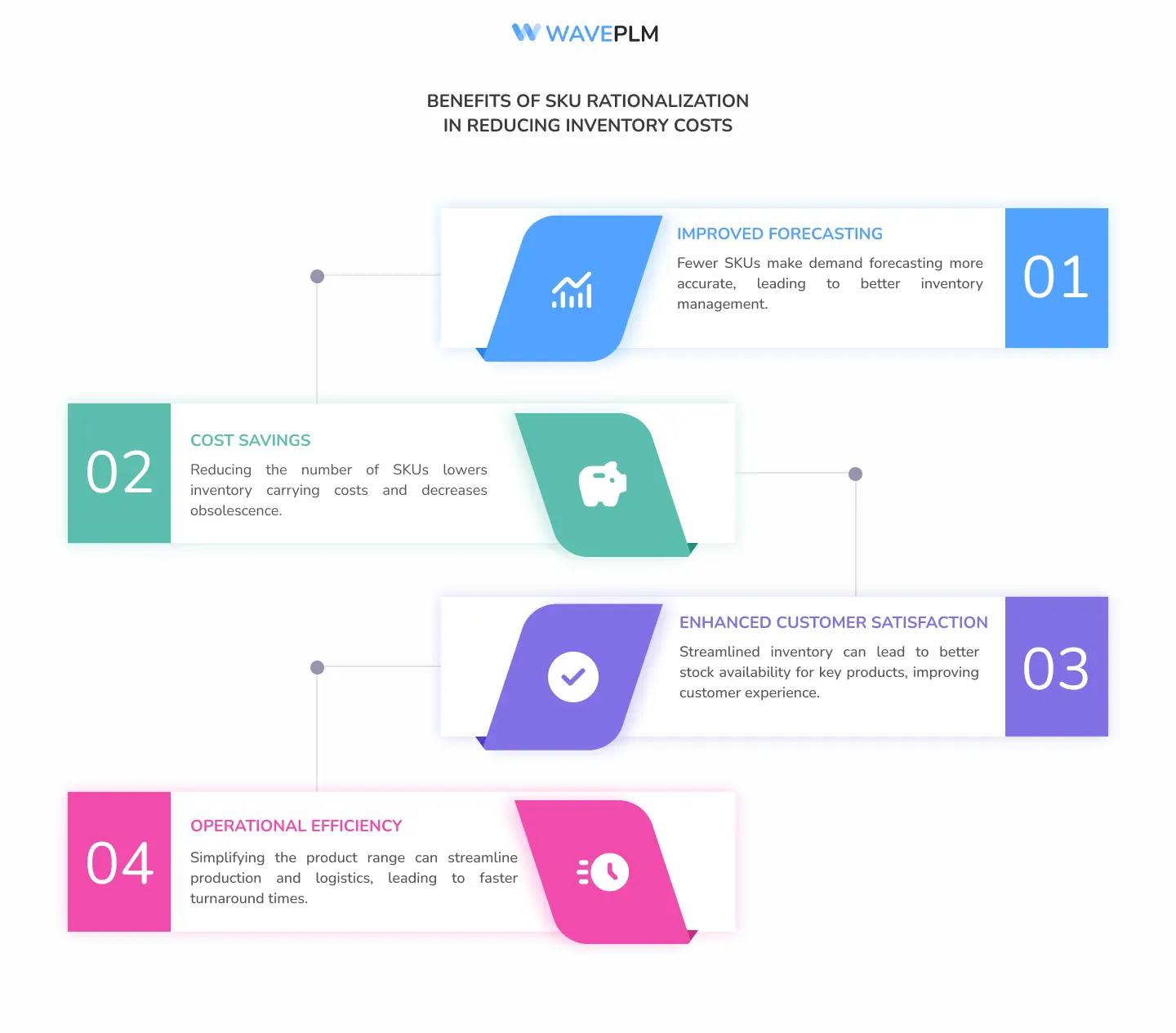
Benefits of SKU Rationalization in Reducing Inventory Costs
- Cost Savings: Reducing the number of SKUs lowers inventory carrying costs and decreases obsolescence. This process is a key aspect of inventory optimization, which improves operational efficiency and overall business performance. By incorporating specific product characteristics such as size, color, and style into SKUs, retailers can enhance inventory management and sales reporting.
- Improved Forecasting: Fewer SKUs make demand forecasting more accurate, leading to better inventory management.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Streamlined inventory can lead to better stock availability for key products, improving customer experience.
- Operational Efficiency: Simplifying the product range can streamline production and logistics, leading to faster turnaround times.
Implementing SKU Rationalization
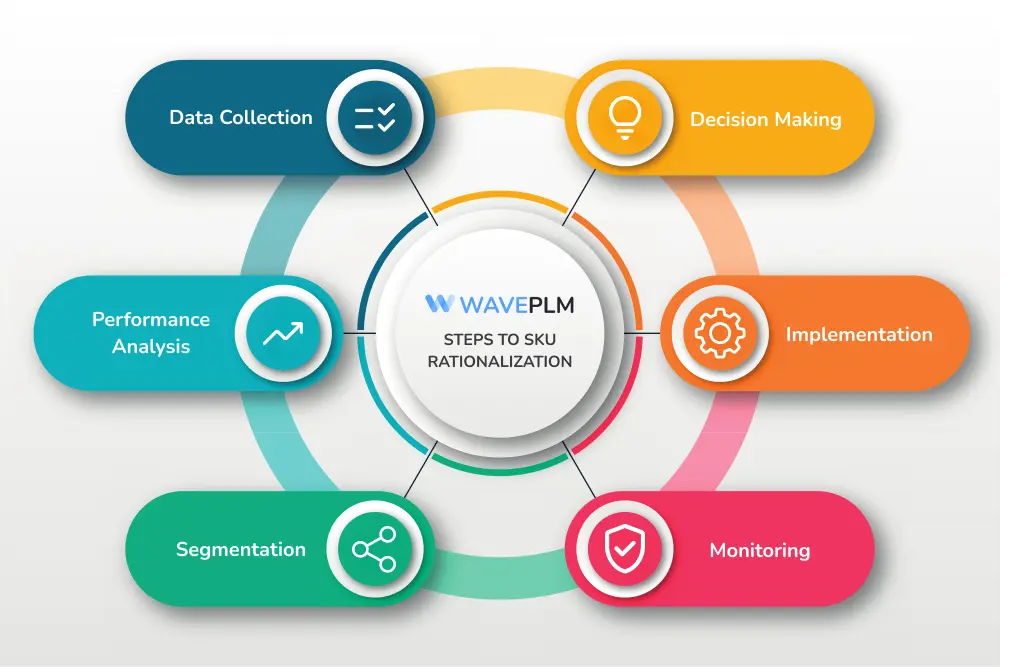
Steps to SKU Rationalization
- Data Collection: Gather comprehensive data on each SKU, including sales performance, production costs, and inventory turnover.
- Performance Analysis: Evaluate each SKU based on profitability, sales volume, and alignment with the brand’s strategic goals. A well-organized SKU structure can adapt to growth, aiding in product differentiation and simplifying complexity.
- Segmentation: Classify SKUs into categories such as core, seasonal, and fringe products.
- Decision Making: Determine which SKUs to retain, which to discontinue, and which to consolidate or modify. Businesses often justify behavior by providing logical reasons for these decisions, even if they are influenced by unconscious biases or instinctual impulses.
- Implementation: Execute the rationalization plan by phasing out selected SKUs and adjusting production and inventory practices.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the performance of the remaining SKUs and adjust the strategy as needed.
Inventory Tracking with SKUs
SKUs help businesses to keep track of their inventory levels and ensure they always have the products their customers need. By using SKUs, businesses can quickly and easily scan products to see what’s in stock and what needs to be reordered. SKUs are a critical component of inventory management and supply chain optimization. SKUs help businesses to manage their inventory and supply chain effectively. SKUs are used by businesses of all sizes to manage their inventory and supply chain. (Keep keywords: inventory management, supply chain, inventory levels, skus, keep track, businesses, inventory, customers)
Role of Product Lifecycle Management in Rationalization
What is PLM?
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is a comprehensive approach to managing the lifecycle of a product from inception, through engineering design and manufacturing, to service and disposal. PLM systems can act as ‘defence mechanisms’ to protect against inefficiencies and threats to business performance. PLM integrates people, processes, business systems, and information to streamline and enhance the entire lifecycle. By using PLM systems, businesses can accurately track inventory, monitor product availability, and set reorder points to prevent shortages.
How PLM Supports SKU Rationalization
PLM systems offer several tools and features that are invaluable in the SKU rationalization process:
- Centralized Data Management: PLM provides a single repository for all product-related data, making it easier to access and analyze information across different SKUs.
- Enhanced Collaboration: PLM systems facilitate better communication and collaboration among departments, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned in the rationalization process.
- Detailed Analytics: Advanced analytics tools within PLM help in evaluating SKU performance based on various metrics such as sales data, production costs, and market trends. Incorporating a check digit in product codes ensures their validity and security, distinguishing the manufacturer and item number.
- Lifecycle Tracking: PLM allows for tracking the entire lifecycle of a product, from design to end-of-life, providing insights into long-term performance and profitability.
- Process Automation: Automating routine tasks within the PLM system can reduce errors and speed up the rationalization process.
- Change Management: PLM systems offer robust change management capabilities, ensuring that any changes to SKUs are systematically implemented and documented.

Benefits of Using PLM for Rationalization
- Improved Decision Making: With comprehensive data and advanced analytics, PLM enables more informed decision-making regarding which SKUs to retain or discontinue.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and automation within PLM reduce the time and effort required for SKU optimization. Using an inventory management system within PLM provides a more efficient method for storing and tracking SKUs compared to traditional methods.
- Better Alignment: PLM ensures that all departments are aligned with the rationalization strategy, reducing the risk of miscommunication and errors.
- Enhanced Agility: With real-time data and efficient processes, fashion companies can quickly adapt to market changes and implement SKU rationalization more effectively.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing SKUs and streamlining operations, PLM helps in achieving significant cost savings.
Case Study: Successful SKU Rationalization Using PLM
Company Overview
Consider a mid-sized fashion company that faced challenges managing an extensive product portfolio. Each product was assigned a unique code, often referred to as a SKU, to help maintain organization and track inventory. With over 10,000 SKUs, the company struggled with high inventory costs, inefficiencies in production, and frequent stockouts of key products.

SKU rationalization – platforme.com
The Challenge
The company needed to streamline its inventory without compromising on its market presence and customer satisfaction. The goal was to reduce SKUs by 30% while improving overall operational efficiency and profitability. While serial numbers are unique to each individual product unit, SKUs can be shared by multiple units for the same product.
The Approach
The company implemented a PLM system to facilitate the SKU rationalization process. Well-structured SKUs facilitated online sales by enhancing product descriptions and helping customers make informed purchasing decisions. The steps included:
- Data Integration: All product data was integrated into the PLM system, providing a centralized source of information.
- Performance Analysis: Using PLM’s analytics tools, the company evaluated each SKU based on sales performance, production costs, and market trends.
- Strategic Segmentation: SKUs were classified into core, seasonal, and fringe categories. Core products were those with consistent demand, seasonal products had high demand during specific periods, and fringe products had low sales and profitability.
- Decision Making: The company decided to retain all core products, streamline seasonal products, and discontinue most fringe products.
- Implementation: The PLM system was used to manage the phase-out of discontinued SKUs and adjust production schedules for the remaining products.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Continuous monitoring was implemented to track the performance of the rationalized product portfolio and make adjustments as needed.
Results
- Reduced Inventory Costs: The company achieved a 35% reduction in inventory carrying costs by eliminating underperforming SKUs. Accurately recording assigned SKUs in the inventory management system enhanced efficiency across various sales channels. This helped to reduce inventory costs by minimizing the need for excess stock and evaluating the profitability of products to determine if they should be retained or removed from inventory.
- Increased Efficiency: Production and logistics operations became more streamlined, leading to a 20% reduction in lead times.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Better stock availability for key products led to a 15% increase in customer satisfaction scores.
- Higher Profitability: Overall profitability improved by 10%, with a more focused and efficient product range.
Best Practices for SKU Rationalization
Leveraging Data Analytics
Effective SKU rationalization heavily relies on data analytics. Fashion companies should invest in robust analytics tools to gather and analyze data on SKU performance. This includes sales data, inventory turnover, production costs, and market trends. By leveraging these insights, companies can make informed decisions about which SKUs to retain or eliminate.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
SKU rationalization is not just a task for the inventory management team. It requires input from various departments including marketing, sales, finance, and production. Cross-functional collaboration ensures that the rationalization strategy aligns with the overall business objectives and that all stakeholders are on board with the changes. While SKUs are specific to manufacturers and used internally, UPC numbers are standardized and universally recognized codes that identify specific products across all sales channels.
Customer-Centric Approach
While SKU optimization focuses on improving operational efficiency and reducing costs, it should not come at the expense of customer satisfaction. Companies should consider customer preferences and buying patterns when deciding which SKUs to retain. Keeping popular and high-demand products in the lineup is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and satisfaction. A logical SKU format, where the beginning characters represent the primary item category followed by specific details, can enhance customer satisfaction by making it easier to locate products.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment for Operational Efficiency
SKU rationalization is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Fashion companies should continuously monitor the performance of their SKUs and make adjustments as needed. Market trends and consumer preferences change over time, and companies need to be agile in responding to these changes.
Point-of-sale systems enable businesses to streamline their selling processes and support operational management, ultimately helping businesses grow.
Strategic Segmentation
Segmenting SKUs into categories such as core, seasonal, and fringe products can help in making more strategic decisions. Core products are those with consistent demand and profitability, while seasonal products have high demand during specific periods. Fringe products typically have low sales and profitability and are prime candidates for discontinuation. Utilizing specific platforms like Lightspeed and Shopify can help businesses manage SKUs, simplify stock tracking, and improve efficiency.
Challenges in SKU Rationalization
Resistance to Change
One of the biggest challenges in SKU rationalization is resistance to change from within the organization. Employees may be attached to certain products or fear that rationalization could lead to job cuts. Effective communication and involving employees in the decision-making process can help mitigate resistance.
Data Quality
The success of SKU rationalization heavily depends on the quality of data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to poor decision-making. Fashion companies need to invest in data management systems and ensure that they have accurate and up-to-date information on all SKUs. Tracking variations in style, such as different colors and sizes, is essential for maintaining accurate inventory records.
Balancing Variety and Efficiency
While rationalizing SKUs can lead to increased efficiency and reduced costs, it can also limit the variety of products offered to customers. Striking the right balance between offering a diverse product range and maintaining operational efficiency is crucial.
Market Dynamics and Supply Chain
The fashion industry is highly dynamic, with trends changing rapidly. What is popular today may not be in demand tomorrow. Companies need to be agile and continuously monitor market trends to ensure that their SKU rationalization strategy remains relevant.
Forecasting Demand and Reorder Points
Using a SKU system, retailers can make more accurate sales and demand forecasting. SKU data can be run through an ecommerce analytics tool to answer questions like which products are selling well and which ones aren’t. SKU data can help retailers identify low-selling items and reduce inventory accordingly. SKU data can help retailers meet customer demand without losing money on dead stock. By analyzing SKU-based data, such as sales volume and inventory turnover, retailers can identify trends, make informed purchasing decisions, and optimize stock levels to maximize profit. Retailers can use SKU data to calculate reorder points and avoid stockouts. (Keep keywords: sku system, sku data, reorder points, sku, use sku, inventory, customer, sales, identify)
Future Trends in SKU Rationalization
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize SKU rationalization. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data and provide insights that are beyond human capability. AI and ML can help in predicting trends, understanding customer preferences, and making more accurate demand forecasts.
Sustainability
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainability is becoming a key consideration in SKU rationalization process. Companies are looking to reduce waste and adopt more sustainable practices. This includes offering a more focused product range and optimizing production processes to minimize environmental impact.
Omni-Channel Integration
With the rise of e-commerce and omni-channel retailing, SKU rationalization is becoming more complex. Companies need to ensure that their product range is optimized across all channels, from physical stores to online platforms. This requires a holistic approach to SKU management and a deep understanding of consumer behavior across different channels.
Personalization
Personalization is another trend that is shaping the future of SKU rationalization. Consumers are increasingly looking for personalized shopping experiences. Companies are using data analytics and AI to offer personalized product recommendations and tailor their product range to meet individual customer preferences.
Rationalization, particularly SKU rationalization, is crucial for fashion businesses aiming to optimize their operations and improve profitability. By systematically evaluating and streamlining product offerings, companies can reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and better meet customer demands. Implementing a PLM system plays a vital role in this process, providing the tools and insights needed for effective rationalization.
In the fast-paced fashion industry, where trends evolve rapidly, and consumer preferences are diverse, rationalization ensures that businesses remain agile, competitive, and profitable. By leveraging the power of PLM, fashion companies can navigate the complexities of SKU rationalization with greater ease and success, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and thriving business.
The key to successful rationalization lies in leveraging data analytics, fostering cross-functional collaboration, and adopting a customer-centric approach. By continuously monitoring and adjusting their product range, fashion companies can stay ahead of market trends and maintain a competitive edge. With the right strategies and tools, SKU rationalization can lead to significant cost savings, improved operational efficiency, and higher profitability, ensuring long-term success in the fashion industry.




