
Clothing and textile export play a crucial role in the fashion industry’s success. Navigating the complexities of textile export requires a comprehensive understanding of market trends, regulations, quality standards, and effective strategies to reach international buyers. In this article, we explore the key steps and considerations for businesses looking to find how to venture into exports within the fashion industry.
Understanding Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Demand for clothes serves as the cornerstone of the export market. Fashion trends, consumer preferences, and societal shifts collectively drive the demand for exported textiles. For instance, the country, growing consciousness towards sustainability in clothing has spurred an increased demand for eco-friendly fabrics such as organic cotton and recycled polyester. This shift towards sustainable fashion has not only reshaped consumer behaviour but also influenced the strategies of textile exporters worldwide.
To excel in export, it’s essential to stay abreast of current market trends and consumer preferences. Fashion is inherently trend-driven, with styles and tastes evolving rapidly. Conducting thorough market research to identify emerging trends, popular styles, and cultural preferences in target export markets is paramount. This understanding of the latest trends allows exporting businesses to tailor their textile products to meet specific consumer demands, thereby increasing their competitiveness in the international market.
Production Capabilities
The production capabilities of a country or region significantly impact its competitiveness in the textile export and import market. Factors such as infrastructure, technology, labour costs, and skill levels determine the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of manufacturing operations. Countries with advanced production facilities and skilled workforce, such as China, Bangladesh, and Vietnam, have traditionally dominated the global export market.
However, emerging economies like Bangladesh, India, and Ethiopia are rapidly gaining traction, due to their lower labour costs and favourable government policies aimed at attracting foreign investment. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as automation and digital manufacturing, are revolutionizing the world of textile production, leading to increased efficiency, precision, and customization capabilities.
Moreover, the decentralization of production hubs and the rise of niche markets offer opportunities for smaller players to carve out their niche in the global textile export market. By focusing on providing specialized products, customizations, or sustainable practices, exporters can differentiate themselves and compete effectively against larger competitors.
Trade Agreements
International trade agreements and tariffs have a profound impact on textile exports, shaping market access, pricing, and competitiveness. Preferential trade agreements, such as free trade agreements (FTAs) and regional trade blocs, facilitate smoother trade flows by eliminating or reducing tariffs and trade barriers between participating countries. For example, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) and the European Union’s Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) grant preferential treatment to eligible exporters, promoting trade and economic cooperation.

On the other hand, trade disputes, protectionist measures, and tariff barriers can disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and hinder market access for exporters. For instance, the ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China have resulted in tariffs on billions of dollars worth of goods, and items including textiles and apparel. Such uncertainties underscore the importance for importers of diversifying market exposure and staying abreast of trade policies and geopolitical developments.
Furthermore, textile exporters today must navigate complex rules of origin and compliance requirements to qualify for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements. Understanding the intricacies of trade agreements and leveraging available trade preferences can confer significant competitive advantages and open up new market opportunities for exporters.
Quality Control
Maintaining stringent quality control standards is essential for textile fabric exporters to uphold product integrity, meet customer expectations, and safeguard brand reputation. Quality encompasses various aspects of the fabric itself, including raw materials, manufacturing processes, workmanship, durability, safety, and environmental sustainability.
For textile exporters, ensuring consistent quality across their product range requires robust quality management systems, rigorous testing protocols, and adherence to international quality standards and certifications. Common quality standards applicable to textiles exporting include ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), ISO 45001 (occupational health and safety), and product-specific certifications such as OEKO-TEX Standard 100 (chemical safety) for textiles and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) for organic textiles exports.
Implementing quality control measures involves comprehensive supplier vetting, in-process inspections, product testing, and post-production audits to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards. Additionally, fostering a culture of quality consciousness among employees and suppliers and investing in training programs can help ensure continuous improvement and adherence to quality objectives.
In today’s hyper-connected world, quality issues or product recalls can quickly tarnish a brand’s reputation and erode consumer trust. Therefore, textile exporters must prioritize quality assurance as a fundamental pillar of their business strategy in order to maintain a competitive edge and sustain long-term success in the global apparel market.
Logistics and Supply Chain Transparency
Efficient logistics, shipping, and supply chain management are critical for textile fabric exporters to ensure seamless operations, timely delivery, and customer satisfaction. A well-optimized supply and value chain encompasses various activities, including sourcing raw materials, production planning, inventory management, transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
In the textile and apparel industry alone, supply chains are often complex and geographically dispersed, involving multiple stakeholders across different countries and continents. Effective coordination and collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and distributors are essential to streamline processes, minimize lead times, and reduce costs.
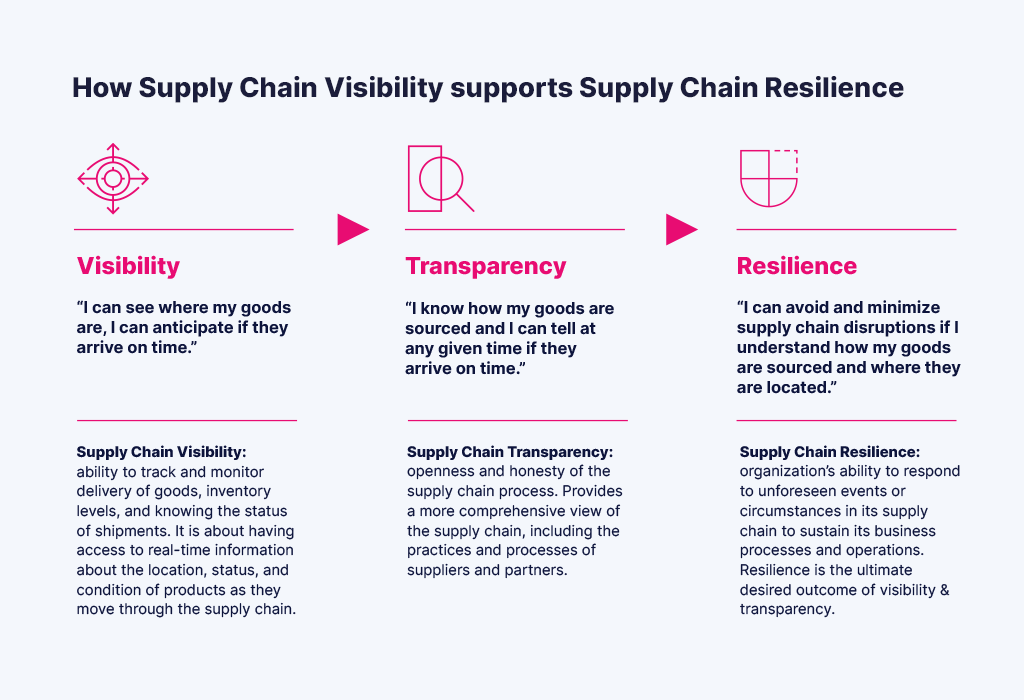
Moreover, supply chain transparency has become increasingly important in response to growing consumer demand for ethically sourced and sustainably produced products. Textile importers and clothing exporters are under pressure to provide visibility into their supply chains, trace the origins of raw materials, and ensure compliance with social and environmental standards.
Technological innovations such as blockchain, RFID (radio-frequency identification), and IoT (Internet of Things) are being leveraged to support this growth and enhance supply chain visibility, traceability, and transparency. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of inventory movements, authentication of product provenance, and verification of compliance with labour and environmental regulations.
Furthermore, adopting sustainable business practices such as lean manufacturing, waste reduction, energy efficiency, and green logistics can see retailers not only minimize environmental impact but also generate cost savings and enhance brand reputation.
Branding and Marketing Strategies
Effective branding and marketing strategies are essential for clothing and textile exporters to differentiate their products, build brand equity, and connect with consumers. A strong brand identity creates an emotional connection with customers, fosters brand loyalty, and influences purchase decisions.
Textile exporters must develop a clear brand positioning and messaging that resonates with their target audience. This involves understanding the unique selling proposition (USP) of their exported products, identifying key consumer segments, and crafting compelling brand stories that communicate value and authenticity.
In conclusion, navigating the global textile export market in fashion demands a comprehensive understanding of the myriad factors at play in total trade, including demand dynamics, production capabilities, trade policies, quality standards, logistics, branding, sustainability practices, regulatory compliance, geopolitical risks, innovation, partnerships, and technology integration. By strategically addressing these factors and embracing change as an opportunity for growth, textile exporters can effectively navigate the complexities of the global apparel import market and emerge as industry leaders poised for sustainable success in the dynamic world of fashion.





Leave a Reply